Question:
2.76 g of silver carbonate on being strongly heated yields a
residue weighing
2.76 g of silver carbonate on being strongly heated yields a
residue weighing
Updated On: Mar 26, 2024
- 2.16 g
- 2.48 g
- 2.32 g
- 2.64 g
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Unlike other metal carbonates that usually decomposes into metal
oxides liberating carbon dioxide, silver carbonate on heating
decomposes into elemental silver liberating mixture of carbon
dioxide and oxygen gas as : M
$ Ag_2CO_3 \, _{\longrightarrow \, \, \, \, }^{Heat} 2Ag (s) + CO_2(g) + \frac{1}{2} O_2(g) $
MW = 276 g $ \hspace26mm $ 2 x 108 = 216 g
Hence, 2.76 g of $Ag_2CO_3 $ on heating will give
$ \frac{216}{216 } \times 2.76 $ = 2.16g Ag as residue.
oxides liberating carbon dioxide, silver carbonate on heating
decomposes into elemental silver liberating mixture of carbon
dioxide and oxygen gas as : M
$ Ag_2CO_3 \, _{\longrightarrow \, \, \, \, }^{Heat} 2Ag (s) + CO_2(g) + \frac{1}{2} O_2(g) $
MW = 276 g $ \hspace26mm $ 2 x 108 = 216 g
Hence, 2.76 g of $Ag_2CO_3 $ on heating will give
$ \frac{216}{216 } \times 2.76 $ = 2.16g Ag as residue.
Was this answer helpful?
1
0
Top Questions on Some basic concepts of chemistry
- A compound X contains 32% of A, 20% of B and remaining percentage of C. Then, the empirical formula of X is:
(Given atomic masses of A=64; B=40; C=32 u)- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Chemistry
- Some basic concepts of chemistry
How many moles of Ba3(PO4)2 will be formed by the reaction of 5 moles of BaCl2 and 3 moles of Na3(PO4).
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Some basic concepts of chemistry
- A sample of a metal oxide has formula $M _{0.83} O _{1.00}$ The metal $M$ can exist in two oxidation states $+2$ and $+3$ In the sample of $M _{0.83} O _{1.00}$, the percentage of metal ions existing in $+2$ oxidation state is___$ \%$ (nearest integer)
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Some basic concepts of chemistry
- 0.5 gm of an organic compound with 60%. Carbon produce ______ gm of \(CO_{2}\) upon complete combustion
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Some basic concepts of chemistry
- When a hydrocarbon A undergoes complete combustion it requires 11 equivalents of oxygen and produces 4 equivalents of water. What is the molecular formula of $A$?
- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Some basic concepts of chemistry
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
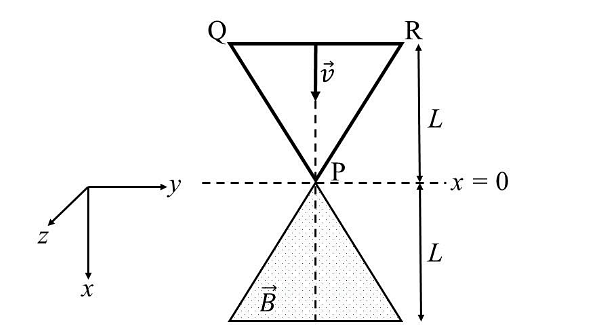
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Chemistry is a vast subject and for understanding its significance we can take help of following points:
- Chemistry plays an important role in understanding various subjects like physics, geology and biology.
- Chemistry is a core branch of science that explains us about the various compositional properties and interaction of matter. It also helps to understand various chemical reactions.
- Chemistry is important in order to understand the behaviour of fertilizers, alkenes, acids, salts, dyes, polymers, drugs, soaps and alloys in organic and inorganic chemistry.
- Chemistry plays an important role in various fields like healthcare, industrial, research, food, and farm activities.
Read More: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Classification of Matter
There are two ways of classifying the matter:
(A) Physical Classification:
Matter can exist in three physical states:
- Solids - have definite volume and definite shape
- Liquids - have definite volume but not definite shape.
- Gases - have neither definite volume nor definite shape.
(B) Chemical Classification:
Based upon the composition, matter can be divided into two main types:
- Pure Substances are defined as a single substance (or matter) which cannot be separated by simple physical methods. Pure substances can be further classified as (i) Elements (ii) Compounds
- Mixtures are the combination of two or more elements or compounds which are not chemically combined together and may also be present in any proportion.



