
Senior Content Specialist | KdTvCV - Apr 25, 2024
Screw gauge is a mechanical tool that allows precise measurement of the diameter, radius, or thickness of a thin wire or a thin metal sheet. It is also known as a micrometer screw gauge. It includes two scales, a Pitch scale, and a Circular scale. Micrometer gauges are highly accurate for measurement in comparison to the Vernier Caliper Scale. Screw gauge measurement can be done using a Micrometer and an Inch Micrometer. A screw gauge is used for the precise measurement of a cylindrical or a spherical object. The screw gauge consists mainly of a U-shaped frame and a spindle (or a screw) attached to the thimble.
Key Terms: Least Count, Pitch, Screw Gauge Measurement, Vernier Caliper, Screw Gauge, Micrometer, Inch Micrometer.
What is Screw Gauge?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Screw gauge is a measuring instrument made out of a calibrated screw used to measure small objects' dimensions. A screw gauge is a type of meteorological instrument used in machining, and mechanical engineering. A screw gauge is used for the precise measurement of thin wires and sheets. It consists of two scales: a Pitch Scale and a Circular Scale.
- Pitch scale is the main scale that measures the distance traveled by the spindle per revolution (in millimeters). It is engraved with vertical lines on the barrel of the instrument.
- Circular scale is horizontally engraved on the thimble. A revolution of the circular scale is equivalent to about half a millimeter of screw displacement.
| Total Screw Gauge Reading = Pitch Scale Reading + Circular Scale Reading x Least Count of the gauge |

Screw Gauge Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The two common parameters of the Screw gauge formula are Pitch and Least Count:
- Pitch: Pitch is the distance moved by the spindle per revolution. This is measured by moving the head scale of the instrument over the pitch scale to complete one full rotation.
| Pitch of screw gauge \(= {Distance \ moved \ by \ screw \over No. \ of \ rotation}\) |
- Least Count: Screw Gauge Least count is the distance that is covered by the tip of the screw when a division of the head scale is turned.
| Least Count of Screw Gauge \(= {Pitch\over No. \ of \ divisions \ on \ the \ circular \ scale}\)
Least count of micrometer screw gauge = \( {1 \ mm\over 100}\)= 0.01 mm |
Screw Gauge Diagram
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The diagram of a screw gauge is as given below:
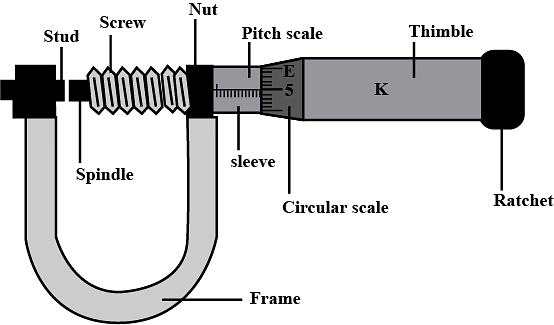
Screw Gauge Diagram
The main elements of a screw gauge are:
- Screw: This is the screw gauge's key component that aids in measurement.
- Anvil: The spindle is moved towards the object to be measured that is put on the anvil.
- Spindle: The spindle will travel towards the anvil as the thimble is rotated.
- Thimble: This is the rotating portion of the screw gauge.
- Thimble lock: This element can be tightened to keep the spindle in position while measuring. It's sometimes referred to as a lock-nut or a lock-ring.
- Ratchet stop: It's utilized to keep the thimble from rotating any further than it needs to.
- Barrel/Main Scale: It's also known as a sleeve or stock, and it's a stationary component with linear or vernier markings on it as seen in the screw gauge diagram.
The barrel of some screw gauge versions is a rotatable cylinder, which allows for zero value by adjusting the cylindrical barrel.
Screw Gauge Measurement Using Micrometer
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The screw gauge measurement through a micrometer can be done using the screw gauge formula. The following steps can be implemented to record the measurement:
- Clean the anvil and the spindle: Take a clean cloth or paper and place it between the spindle and the anvil. Tighten the setup slightly until the paper or cloth becomes stuck, then pull it out while cleaning the setup. This step aids in obtaining an exact measurement.
- Place the object between the spindle and anvil: Carefully place the thing between the anvil and the spindle. As the anvil is stationary, put the object that is to be measured against it. The object should be appropriately positioned so that it does not move while the measurements are taken.
- Rotate the ratchet counterclockwise to tighten it: Make sure the thimbles' zero is parallel to the scale's line on the sleeve.
- Tighten the spindle with the object in the middle: When you rotate the thimble, it clicks. Increase effort until it clicks three times.
- Lock the thimble: While the object is in the middle, lock the thimble. The spindle can be moved even though the thimble is closed. This will help you get the precise measurement.
- Take the object out: Carefully take out the object without compromising the accuracy of the screw gauge.
- Note the reading: Before you unlock the spindle of the screw gauge, note the reading on it as seen in the screw gauge diagram.
| Note: Make a note that if the screw gauge loosens even in a single step, you have to re-measure the entire structure. |
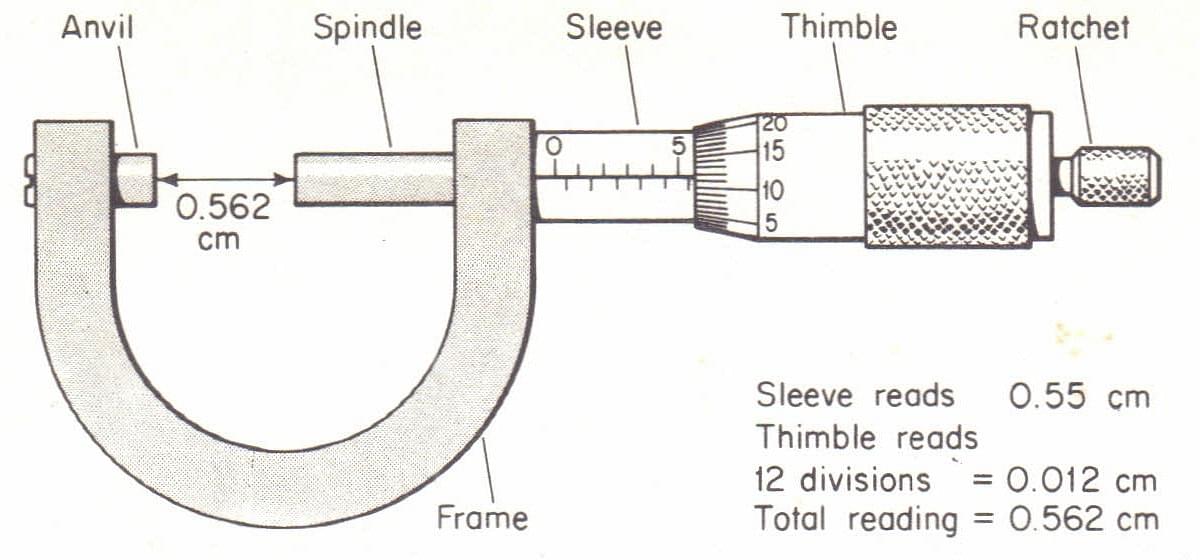
Screw Gauge Measurement ExampleLet’s assume a screw gauge with the least count of 0.01 mm. What is its total reading? Solution: The main scale reading is 2.5 mm and the circular scale reading is 38. |
Screw Gauge Measurement Using Inch Micrometer
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The screw gauge measurement using an inch micrometer can be done by:
- Different scales of thimbles: There are many distinct scales on the thimble: One hundred thousand, or one-tenth of an inch, or 0.100 in decimal notation. Between the numbers, three lines equal to twenty-five thousandths of an inch are there, expressed in decimal as 0.025.
The equally spaced lines depict one-thousandth of an inch, denoted as 0.001 in decimal notation. - Sleeves have whole numbers: The whole number scale defined by the lines on the sleeve represents a measurement of ten-thousandths of an inch, expressed as 0.0001 in decimal notation. The number shown at the end is a thousandth representation.
For example, if the last digit is 6, the final representation would be 0.500. - Note the number of lines after the whole number: Take note of the markings next to the 100,000th mark and multiply it by 0.25.
- Note the marking corresponding to the thimble scale marking: Note the marking closest to it and beneath the measurement line.
- Add the numbers: The three numbers that are noted down in the previous step should be observed and added using the screw gauge formula.
Working Principle of Screw Gauge
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Screw gauge operates on the principle of a screw. The screw gauge formula measures the rotation of the screw, thereby converting smaller distances into larger ones. Two parameters are used for screw gauge measurement – pitch and least count.
- The ratio of the moved distance to the number of rotations is known as the pitch of the screw gauge.
- The ratio of pitch to the total number of divisions that is there on the circular scale is known as the screw gauge least count.

A differential screw is a crucial component of an analog screw gauge that enables small magnitudes. These screws have several threads, each corresponding to axial movement when spun one at a time. That is, each 360 degrees spin of the screw spans a minimal axial distance.
- This distance is referred to as the screw's lead or pitch of the screw gauge. Even if the object to be measured is tiny, the size of the thing can be determined by turning the thimble, which rotates the screw.
- The minute dimension is transformed into more extensive rotations that are much easier to comprehend.
- The dimension of the wire measured is displayed on an LCD screen in digital screw gauges.
Uses of Screw Gauge
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
There are various uses of screw gauge which are as follows:
- With an accuracy of 0.001cm, a screw gauge is used to measure the diameter of circular objects, primarily wires.
- The radius of wires and other circular objects can be found using a screw gauge.
- A screw gauge is also used to determine the thickness of a piece of paper.
- Metal sheet and glass slab thickness can be identified using a screw gauge.
- Uniform thickness of any shape can be found using a screw gauge.
Also Read:
Things to Remember
- A screw gauge is a measuring instrument made out of a calibrated screw used to measure small objects' dimensions.
- Screw gauge measurement can be done using Micrometers and Inch Micrometers.
- Any metal sheet's diameter and radius are measured with a screw gauge. It's a U-shaped tool with a screw-on one end.
- In every screw gauge, two parameters are employed for measurement purposes. They are the screw gauge's pitch and least count.
- The ratio of the moved distance to the number of rotations is known as the pitch.
- Pitch = (distance)/(no. of rotations given).
- The ratio of pitch to the total number of divisions that is there on the circular scale is known as the least count.
- Least count = (pitch)/(total no. of divisions on the circular scale).
Sample Questions
Ques 1. What is a screw gauge used for? (2 marks)
Ans. A screw gauge, also known as a micrometer, is a measuring instrument made out of a calibrated screw. The screw gauge formula is used:
- To measure the dimensions of small objects.
- In machining, mechanical engineering, and other applications.
- It is used to measure the thickness and diameter of objects that are very small with great accuracy for eg. Wires, paper sheets, metal sheets, etc.
Ques 2. What is the least count of the screw gauge? (1 mark)
Ans. The screw gauge’s least count is defined as the distance traveled by the screw's tip when it is spun through one division of the head scale.
Ques 3. The least count of the main scale of a screw gauge is 1mm. The minimum number of divisions on its circular scale required to measure 5 μm diameter of wire is: (5 Marks)
a) 50
b) 100
c) 200
d) 500
Ans. It is given in the question that,
The least count of the main scale of a screw gauge is 1mm.
We know that the pitch of the screw gauge is equal to the least count of the main scale of a screw gauge, that is
P = 1mm
On converting it into an SI unit that is, in meters, we get
P = 10−3m
It is also given that the diameter of wire measured with that screw gauge is 5μm.
We have seen that the given diameter of the wire is much smaller than the least count of the main scale of the screw gauge. So, for the minimum number of divisions of a circular scale:
The least count of screw gauge is equal to the diameter of the wire, that is
L.C = 5μm
On converting it into an SI unit that is, in meters, we get
L.C = 5×10−6 m
Now by applying the formula, we get
L.C = P/N
Where L.C is the least count of screw gauge
P is the pitch of the screw gauge
N is the minimum number of the division on the circular scale of the screw gauge.
On putting all the values in that formula, we get,
⇒ 5×10−6 = 10−3/N
On further solving that, we get
⇒N = 1000/5
⇒N = 200
Thus, the minimum number of the division on the circular scale of the screw gauge is 200.
Therefore, the correct answer is C.
Ques 4. How do you read a screw gauge? (1 mark)
Ans. A screw gauge measurement can be read in two parts:
- First part is measured by the main scale on the sleeve
- Second part is measured by the rotating vernier scale on the thimble
Then measurement can be calculated using the screw gauge formula.
Ques 5. What is the least count of a micrometer screw gauge? (1 mark)
Ans. Least count (LC) of micrometer screw gauge = (1 mm)/(100) = 0.01 mm
Ques 6. Define ‘Precision Instruments’? Give examples (2 marks)
Ans. Precision instruments are devices that can measure the smallest fraction of a millimetre. For example, Vernier Callipers and Screw Gauge
Ques 7. Write down the screw gauge formula for least count and pitch. (2 marks)
Ans. The Least Count and Pitch are used for screw gauge measurement:
- Pitch of the screw gauge = (distance moved by a screw)/(no. of rotations given)
- Least count of the screw gauge = (pitch)/(total no. of divisions on the circular scale)
Ques 8. How is screw gauge measured? (2 marks)
Ans. The Screw Gauge is defined by the thickness (diameter) of the un-threaded part of the screw known as the shank. Ordinarily, the head size is roughly twice the diameter of the shank, although there are some exceptions associated with hybrid, hardened, DIN Standard (metric) and imported screws.
Ques 9. The pitch of a screw gauge is 1 mm and there are 100 divisions on the circular scale. While measuring the diameter of a wire, the linear scale reads 1 mm and the 47th division on the circular scale coincides with the reference line. The length of the wire is 5.6 cm. Find the curved surface area (in cm) of the wire in significant figures. (5 marks)
Ans. The distance moved on the linear scale when the circular scale makes one complete rotation is p = 1 mm (pitch). The number of divisions on the circular scale is N = 100. Thus, one division on the circular scale is \(LC = \frac{p}{N} = \frac{1}{100} = 0.01 mm\). The linear scale reading (LSR) is 1 mm and the circular scale reading (CSR) is 47. Thus, the diameter of the wire is:
d = LSR + CSR × LC
= 1 + 47 × 0.01
= 1.47 mm
= 0.147 cm
The curved surface area of the cylinder is
\(A = \pi dl = 3.14 (0.147)(5.6) = 2.5848 cm^2\)
Ques 10. What is the minimum measurement of a screw gauge? (2 marks)
Ans. The fundamental distinction between the screw gauge and the vernier caliper is that the screw gauge is only used for external measurements, while the vernier calliper is used for external and internal measurements. The Vernier Caliper's minimum count is 0.01 mm while the screw gauge's minimum count is 0.001 mm.
Ques 11. A screw gauge with a 0.5 mm pitch and a circular scale with 50 divisions is used to measure the thickness of a thin Aluminium sheet. Before measuring, it is found that when two jaws of the screw gauge are brought together, the 45th division coincides with the main scale and the zero of the main scale is barely visible. What is the thickness of the sheet if the the main scale reading is 0.5 mm and the 25th division coincides with the main scale line? (3 marks)
Ans. Least count = pitch/no. of division on circular scale
= 0.5 mm/50
= 0.01 mm
Negative zero error = – 5 × LC = -5 × 0.01
= -0.05 mm
Measured value
= Main scale reading + Screw gauge reading – Zero error
= 0.5mm + 25 × 0.01mm – (-0.05mm)
= 0.75mm + 0.05mm
= 0.80mm
Ques 12. What is the zero error of a screw gauge? (2 marks)
Ans. If the zero line on the circular scale of screw gauge does not coincide with zero on the linear scale when the screw of the circular scale is fully tightened or moved, the error is known as zero error of the screw gauge.
Ques 13. What is backlash error? (2 marks)
Ans. While reversing the direction of rotation of the thimble, if the tip of the screw doesn’t start immediately moving in the opposite direction but remains stationary; it is known as backlash error. This happens due to the wear and tear of screw threads.
Ques 14. What are the components of the screw gauge? (2 marks)
Ans. The components of the screw gauge are Screw, Spindle, Ratchet stop, Frame, Anvil, Barrel, Thimble lock, and Thimble.
Ques 15. Why screw gauge is called micrometer? (1 mark)
Ans. A screw gauge is also known as a micrometer as it measures the lengths of the order of 1 micrometer.
Ques 16. How do you calculate screw gauge reading? (1 mark)
Ans. The screw gauge reading can be calculated using the screw gauge formula which is Total Reading = Pitch Scale Reading + Circular Scale Reading x LC of the gauge.
Ques 17. What is the positive and negative error of a screw gauge? (2 marks)
Ans. When the zero of the circular scale, the error is negative. So, the zero correction will be positive. When the zero error is positive, it will be subtracted from the value that is measured and when the zero error is negative zero error, it will be added to the reading.
Ques 18. What is the difference between a vernier caliper and a screw gauge? (2 marks)
Ans. A screw gauge is only used for the external measurement while a vernier caliper is used for both external and internal measurement.
The least count of a screw gauge is 0.01 cm while the least count of a vernier caliper is 0.001 cm.
Ques 19. What is the pitch scale? (1 mark)
Ans. A scale in millimeters that is parallel to the axis of the thimble is known as the pitch scale. It is the main scale of a screw gauge. A scale on the thimble is known as the head scale. The head scale is divided into 50 to 100 equal parts.
Ques 20. What are the two scales of a screw gauge? (2 marks)
Ans. The two scales of a screw gauge are –
- Rotating or circular scale on its rotating cylindrical part
- Main Scale or Sleeve scale is found on the stationary sleeve.
Also check:





VbyRUy