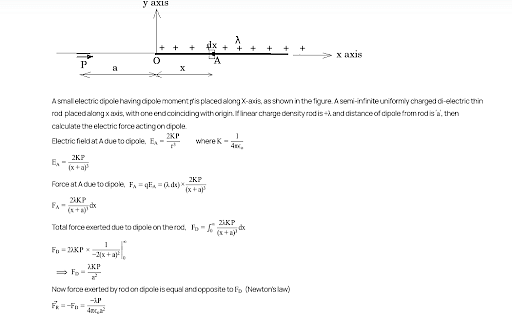
Question:
Two point dipoles $p \hat{k}$ and $\frac{p}{2} \hat{k}$ are located at $(0,0,0)$ and $(1\, m , 0,2\, m )$ respectively. The resultant electric field due to the two dipoles at the point $(1 \,m , 0,0)$ is
Two point dipoles $p \hat{k}$ and $\frac{p}{2} \hat{k}$ are located at $(0,0,0)$ and $(1\, m , 0,2\, m )$ respectively. The resultant electric field due to the two dipoles at the point $(1 \,m , 0,0)$ is
Updated On: Apr 22, 2024
- $\frac{9 p}{32 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \hat{k}$
- $\frac{-7 p}{32 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \hat{k}$
- $\frac{7 p }{32 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \hat{ k }$
- none of these
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
The given point is on axis of $\frac{\hat{p}}{2}$ dipole and at equatorial line of $\hat{p}$ dipole so that field at given point is $\left(\hat{E}_{1}+\hat{E}_{2}\right)$
$\vec{E_{1}}=\frac{2 K(p 2)}{2^{3}}=\frac{K p}{8}(+\hat{k})$
$\vec{E_{2}}=\frac{K p}{1}(-\hat{k}) $
$\vec{E_{1}}+\vec{E_{2}}=-\frac{7}{8} K p(-\hat{k})=-\frac{7 p}{32 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \hat{k}$
$\vec{E_{1}}=\frac{2 K(p 2)}{2^{3}}=\frac{K p}{8}(+\hat{k})$
$\vec{E_{2}}=\frac{K p}{1}(-\hat{k}) $
$\vec{E_{1}}+\vec{E_{2}}=-\frac{7}{8} K p(-\hat{k})=-\frac{7 p}{32 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \hat{k}$
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Electric Dipole
- A small electric dipole \(\bar{P_0}\), having a moment of inertia I about its center, is kept at a distance r from the center of a spherical shell of radius R. The surface charge density \(\sigma\)is uniformly distributed on the spherical shell. The dipole is initially oriented at a small angle 𝜃 as shown in the figure. While staying at a distance r, the dipole is free to rotate about its center.If released from rest, then which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
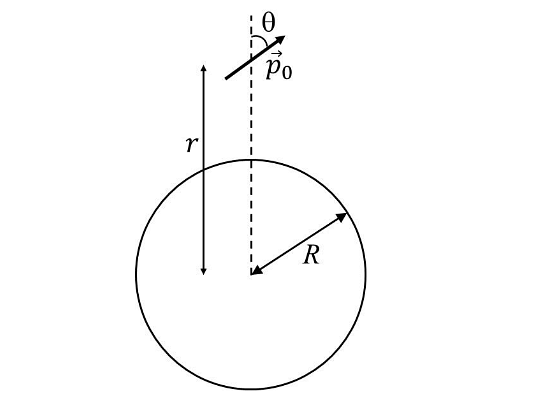
If released from rest, then which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- An electric dipole of dipole moment p is placed at the origin of the coordinate system along the z-axis. The amount of work required to move a charge 'q' from the point (a,0,0) to the point (0,0,a) is
- WBJEE - 2023
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- In the situation shown in the diagram, magnitude of q << | Q | and r>>a. The net force on the free charge -q and net torque on it about O at the instant shown are respectively
[ p = 2aQ is the dipole moment ]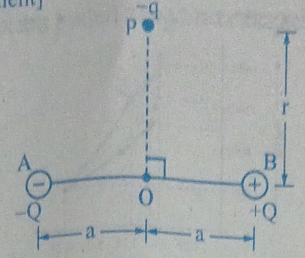
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
Consider a positively charged infinite cylinder with uniform volume charge density \(\rho>0\). An electric dipole consisting of +Q and -Q charges attached to opposite ends of a massless rod is oriented as shown in the figure. At the instant as shown in the figure, the dipole will experience,
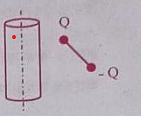
- WBJEE - 2023
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- The drift velocity of the electron is directly proportional to the:
- CUET (UG) - 2022
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
View More Questions
Questions Asked in VITEEE exam
- Two identical blocks A and B, each of mass 'm' resting on a smooth floor are connected by a light spring of natural length L and spring constant K, with the spring at its natural length. A third identical block 'C' (mass m) moving with a speed v along the line joining A and B collides with A. the maximum compression in the spring is
- VITEEE - 2023
- work, energy and power
- Assertion :
The binding energy of the nucleus increases with the increase in atomic number.
Reason :
Heavier elements have a greater number of non-radioactive isotopes than radioactive isotopes. - The half-life of radioactive radon is 3.8 days. The time at the end of which \(\frac{1}{20}th\) of the Radon sample will remain undecayed is (given log10e=0.4343)
- Which element has more electron gain enthalpy among chalcogen group?
- VITEEE - 2022
- sulphur
- Coin is tossed till heads is obtained what is expectation of no. of coin tosses
- VITEEE - 2022
- Random Variables
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Electric Dipole
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite point charges -q and q, separated by a distance of 2a. The direction from q to -q is said to be the direction in space.
p=q×2a
where,
p denotes the electric dipole moment, pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge.
Force Applied on Electric Dipole