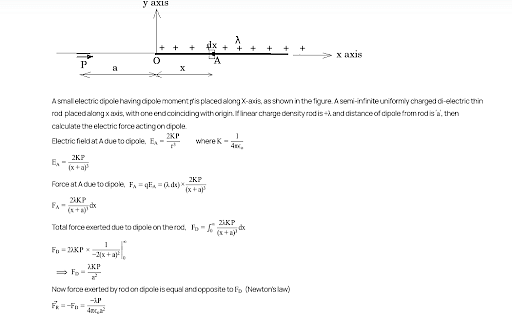
Question:
Two point dipoles of dipole moment $\overrightarrow{p_{1}}$ and $\overrightarrow{p_{2}}$ are at a distance $x$ from each other and $\overrightarrow{p_{1}} \left|\right| \overrightarrow{p_{2}}.$ The force between the dipoles is :
Two point dipoles of dipole moment $\overrightarrow{p_{1}}$ and $\overrightarrow{p_{2}}$ are at a distance $x$ from each other and $\overrightarrow{p_{1}} \left|\right| \overrightarrow{p_{2}}.$ The force between the dipoles is :
Updated On: Aug 14, 2024
- $\frac{1}{4\pi\varepsilon_{0}} \frac{4p_{1}p_{2}}{x^{4}}$
- $\frac{1}{3\pi\varepsilon_{0}} \frac{8p_{1}p_{2}}{x^{3}}$
- $\frac{1}{4\pi\varepsilon_{0}} \frac{6p_{1}p_{2}}{x^{4}}$
- $\frac{1}{4\pi\varepsilon_{0}} \frac{8p_{1}p_{2}}{x^{4}}$
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
Force of interaction
$F = \frac{1}{4\pi\varepsilon_{0}}. \frac{3p_{1}p_{2}}{r^{4}}$
$F = \frac{1}{4\pi\varepsilon_{0}}. \frac{3p_{1}p_{2}}{r^{4}}$
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Electric Dipole
- A small electric dipole \(\bar{P_0}\), having a moment of inertia I about its center, is kept at a distance r from the center of a spherical shell of radius R. The surface charge density \(\sigma\)is uniformly distributed on the spherical shell. The dipole is initially oriented at a small angle 𝜃 as shown in the figure. While staying at a distance r, the dipole is free to rotate about its center.If released from rest, then which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
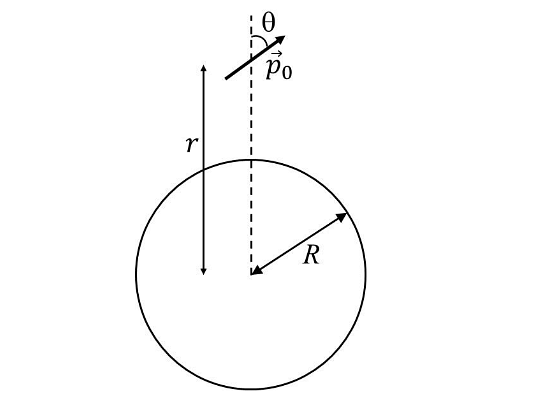
If released from rest, then which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- An electric dipole of dipole moment p is placed at the origin of the coordinate system along the z-axis. The amount of work required to move a charge 'q' from the point (a,0,0) to the point (0,0,a) is
- WBJEE - 2023
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- In the situation shown in the diagram, magnitude of q << | Q | and r>>a. The net force on the free charge -q and net torque on it about O at the instant shown are respectively
[ p = 2aQ is the dipole moment ]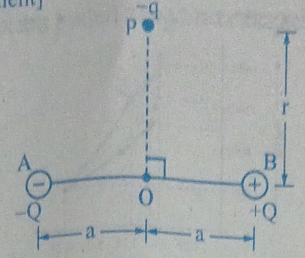
- KCET - 2023
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
Consider a positively charged infinite cylinder with uniform volume charge density \(\rho>0\). An electric dipole consisting of +Q and -Q charges attached to opposite ends of a massless rod is oriented as shown in the figure. At the instant as shown in the figure, the dipole will experience,
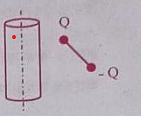
- WBJEE - 2023
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
- The drift velocity of the electron is directly proportional to the:
- CUET (UG) - 2022
- Physics
- Electric Dipole
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- Let \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k}, \quad \vec{b} = -\hat{i} - 8\hat{j} + 2\hat{k}, \quad \text{and} \quad \vec{c} = 4\hat{i} + c_2\hat{j} + c_3\hat{k} \]be three vectors such that \[\vec{b} \times \vec{a} = \vec{c} \times \vec{a}.\]If the angle between the vector $\vec{c}$ and the vector $3\hat{i} + 4\hat{j} + \hat{k}$ is $\theta$, then the greatest integer less than or equal to $\tan^2 \theta$ is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- 10 mL of gaseous hydrocarbon on combustion gives 40 mL of CO\(_2\)(g) and 50 mL of water vapour. The total number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon is ______ .
- JEE Main - 2024
- Hydrocarbons
- If each term of a geometric progression \( a_1, a_2, a_3, \dots \) with \( a_1 = \frac{1}{8} \) and \( a_2 \neq a_1 \), is the arithmetic mean of the next two terms and \( S_n = a_1 + a_2 + \dots + a_n \), then \( S_{20} - S_{18} \) is equal to
- JEE Main - 2024
- Arithmetic Mean
A body of mass 1000 kg is moving horizontally with a velocity of 6 m/s. If 200 kg extra mass is added, the final velocity (in m/s) is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- speed and velocity
- $\textbf{Choose the correct statements about the hydrides of group 15 elements.}$
A. The stability of the hydrides decreases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 > \text{PH}_3 > \text{AsH}_3 > \text{SbH}_3 > \text{BiH}_3\)
B. The reducing ability of the hydrides increases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 < \text{PH}_3 < \text{AsH}_3 < \text{SbH}_3 < \text{BiH}_3\)
C. Among the hydrides, \(\text{NH}_3\) is a strong reducing agent while \(\text{BiH}_3\) is a mild reducing agent.
D. The basicity of the hydrides increases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 < \text{PH}_3 < \text{AsH}_3 < \text{SbH}_3 < \text{BiH}_3\)
Choose the most appropriate from the option given below:- JEE Main - 2024
- p -Block Elements
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Electric Dipole
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite point charges -q and q, separated by a distance of 2a. The direction from q to -q is said to be the direction in space.
p=q×2a
where,
p denotes the electric dipole moment, pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge.
Force Applied on Electric Dipole