Two identical glass rods $S_1$ and $S_2$ (refractive index = 1.5) have one convex end of radius of curvature 10 cm. They are placed with the curved surfaces at a distance d as shown in the figure, with their axes (shown by the dashed line) aligned. When a point source of light P is placed inside rod $S_1$ on its axis at a distance of 50 cm from the curved face, the light rays emanating from it are found to be parallel to the axis inside $S_2$. The distance d is
- 60 cm
- 70 cm
- 80 cm
- 90 cm
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on Ray optics and optical instruments
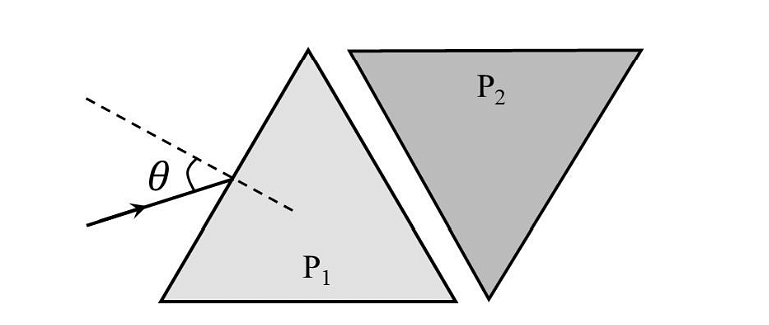
- Two equilateral-triangular prisms \(P_1 \)and \(P_2\) are kept with their sides parallel to each other, in vacuum, as shown in the figure. A light ray enters prism \(P_1\) at an angle of incidence 𝜃 such that the outgoing ray undergoes minimum deviation in prism \(P_2\). If the respective refractive indices of \(P_1\) and\( P_2\) are \(√ 3 /2\) and \(√3\), then \(\theta = sin{−1}[\sqrt \frac{ 3}{ 2} sin ( \frac{\pi}{B} )],\) where the value of \(\beta\) is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- A monochromatic light wave is incident normally on a glass slab of thickness as shown in the figure. The refractive index of the slab increases linearly from n1 to n2 over the height of h. Which of the following statements is/are true about the light wave emerging out of the slab?

Monochromatic light wave
- JEE Advanced - 2023
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- An object is placed Infront of a plane mirror 12 cm away from it. The object is kept fixed while the plane mirror is shifted towards the object by a distance of 4 cm. The length of shift in the position of image is equal to ___________ cm.
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
A person of height 1.6 m is walking away from a lamp post of height 4 m along a straight path on the flat ground. The lamp post and the person are always perpendicular to the ground. If the speed of the person is 60 cm s−1, the speed of the tip of the person’s shadow on the ground with respect to the person is _______ cm s−1.
- JEE Advanced - 2023
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- Two thin lenses are of same focal length (f), but one is convex and the other is concave. When they are placed in opposite with each other, the equivalent focal of the combination will be:
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Physics
- Ray optics and optical instruments
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- A region in the form of an equilateral triangle (in x-y plane) of height L has a uniform magnetic field 𝐵⃗ pointing in the +z-direction. A conducting loop PQR, in the form of an equilateral triangle of the same height 𝐿, is placed in the x-y plane with its vertex P at x = 0 in the orientation shown in the figure. At 𝑡 = 0, the loop starts entering the region of the magnetic field with a uniform velocity 𝑣 along the +x-direction. The plane of the loop and its orientation remain unchanged throughout its motion.
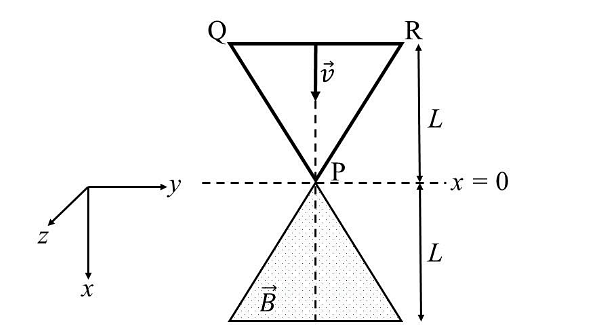
Which of the following graph best depicts the variation of the induced emf (E) in the loop as a function of the distance (𝑥) starting from 𝑥 = 0? - Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A group of 9 students, s1, s2,…., s9, is to be divided to form three teams X, Y and Z of sizes 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Suppose that s1 cannot be selected for the team X and s2 cannot be selected for the team Y. Then the number of ways to form such teams, is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Combinations
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let X be a random variable, and let P(X = x) denote the probability that X takes the value x. Suppose that the points (x, P(X = x)), x = 0,1,2,3,4, lie on a fixed straight line in the xy -plane, and P(X = x) = 0 for all x ∈ R - {0,1,2,3,4}. If the mean of X is \(\frac{5}{2}\) , and the variance of X is α, then the value of 24α is ______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Probability
Concepts Used:
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Optics, deals with the determination of behaviour and the properties of light, along with its interactions with the matter and also with the instruments that are used to detect it.
Ray optics is also known as the geometrical optics and it is a branch of science which describes light propagation.
Reflection is the change in direction of light at an interface in-between two different media so that the wave-front returns into a medium from which it was originated.
Speed of light is the rate at which the light travels in free space.
A phenomenal change in image formed when the light is passed from one medium to another which is called Refraction.
Total Internal Reflection is the reflection of light when the light ray enters into a rarer medium from a denser medium and the angle of incidence is higher than the critical angle of incidence then that light ray will be reflected back to the denser medium.
Read More: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments



