Question:
The total vapour pressure of an ideal binary liquid mixture of benzene and toluene is 0.3 bar. The vapour pressure of pure benzene is 0.5 bar and that of toluene is 0.2 bar. The mole fraction of benzene in this mixture is _______.
(rounded off to two decimal places)
The total vapour pressure of an ideal binary liquid mixture of benzene and toluene is 0.3 bar. The vapour pressure of pure benzene is 0.5 bar and that of toluene is 0.2 bar. The mole fraction of benzene in this mixture is _______.
(rounded off to two decimal places)
(rounded off to two decimal places)
Updated On: Oct 1, 2024
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Correct Answer: 0.32 - 0.34
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is: 0.32 to 0.34 (approx).
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Phase equilibria
- Consider a vapour-liquid mixture of components A and B that obeys Raoult's law. The vapour pressure of A is half that of B. The vapour phase concentrations of A and B are 3 mol m\(^{-3}\) and 6 mol m\(^{-3}\), respectively. At equilibrium, the ratio of the liquid phase concentration of A to that of B is:
- The vapor pressure of a dilute solution of a non-volatile solute and the vapor pressure of the pure solvent at the same temperature are P and P*, respectively. \(\frac{P^*-P}{P^*}\) is equal to
(Assume that the vapor phase behaves as an ideal gas)- IIT JAM CY - 2023
- Physical Chemistry
- Phase equilibria
- The phase diagram of water is best represented by
- IIT JAM CY - 2022
- Physical Chemistry
- Phase equilibria
- At constant temperature, 6.40 g of a substance dissolved in 78 g of benzene decreases the vapor pressure of benzene from 0.125 atm to 0.119 atm. The molar mass of the substance is ____g mol-1. (round off to one decimal place)
[Given: Mol. wt. of benzene = 78 g mol-1]- IIT JAM CY - 2022
- Physical Chemistry
- Phase equilibria
Questions Asked in IIT JAM CY exam
- A salt QCl of a certain metal Q is electrolyzed to its elements. 40 g of metal Q is formed at an electrode. The volume of Cl2 formed at the other electrode at 1 atm pressure and 298 K is _______ litres. (rounded off to one decimal place)
[Given: The gas constant 𝑅 = 0.082 L atm mol−1 K−1 , the molar mass of Q is 40 g mol−1 and Cl2 is assumed to be an ideal gas]- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Electrochemistry
- Exhaustive hydrogenation of the following compound
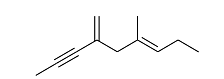
under Pd/C generates a saturated hydrocarbon as the product.
The number of stereoisomers possible for this product is _______.- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Stereochemistry
- In the cell reaction
P+(𝑎𝑞)+Q(𝑠)→P(𝑠)+Q+(𝑎𝑞)
the EMF of the cell, 𝐸𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑙 is zero. The standard EMF of the cell, 𝐸𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑙 is
[Given:
Activities of all solids are unity.
Activity of P+(𝑎𝑞) is 2 M. Activity of Q+(𝑎𝑞) is 1 M.
𝑅 = universal gas constant; 𝑇 = temperature; 𝐹 = Faraday constant]- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Electrochemistry
- A system undergoes one clockwise cycle from point X back to point X as shown in the figure below:
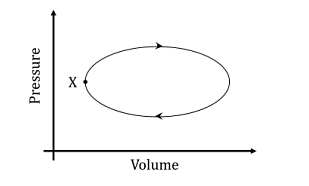
The correct statement about this process is- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Thermodynamics
- The unit cell of a two-dimensional square lattice with lattice parameter a is indicated by the dashed lines as shown below:
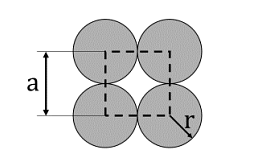
The percentage (%) area occupied by the grey circles (of radius r) inside the unit cell is _______. (rounded off to the nearest integer)- IIT JAM CY - 2024
- Solid State
View More Questions



