The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction
$MgO (s)+2 HCl (a q) \longrightarrow MgCl _{2}(a q)+ H _{2} O (l)$ will be
- less than $-57.33 \,kJ \,mol ^{-1}$
- $-57.33 \,kJ \,mol ^{-1}$
- greater than $-57.33\, kJ\, mol ^{-1}$
- $57.33\, kJ\, mol ^{-1}$
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on Laws of thermodynamics
- The quantity which changes with temperature:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Chemistry
- Laws of thermodynamics
- Which one of the following statements is correct in the context of thermodynamics?
- GATE BT - 2024
- Fundamentals of Biological Engineering
- Laws of thermodynamics
- Consider the following volume−temperature (V−T) diagram for the expansion of 5 moles of an ideal monoatomic gas.
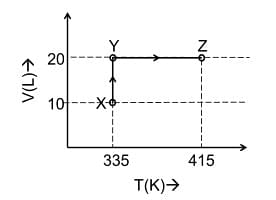
Considering only P-V work is involved, the total change in enthalpy (in Joule) for the transformation of state in the sequence X→Y→Z is ______.
[Use the given data: Molar heat capacity of the gas for the given temperature range, CV,m = 12 J K−1mol−1 and gas constant, R=8.3 JK−1 mol−1]- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Chemistry
- Laws of thermodynamics
- Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: In an Ellingham diagram, the oxidation of carbon to carbon monoxide shows a negative slope with respect to temperature
Reason R: CO tends to get decomposed at higher temperature
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Laws of thermodynamics
- A certain amount of gas of volume $V$ at $27^{\circ} C$ temperature and pressure $2 \times 10^7 Nm ^{-2}$ expands isothermally until its volume gets doubled Later it expands adiabatically until its volume gets redoubled The final pressure of the gas will be (Use $\gamma=15$ )
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Laws of thermodynamics
Questions Asked in JIPMER exam
- Binomial nomenclature was first introduced by
- JIPMER - 2015
- KCET - 2022
- Diversity In The Living World
- A convex lens $'A'$ of focal length $20\, cm$ and a concave lens $'B'$ of focal length $5\, cm$ are kept along the same axis with a distance $'d'$ between them. If a parallel beam of light falling on $'A'$ leaves $'B'$ as a parallel beam, then the distance $'d'$ in cm will be :
- JIPMER - 2021
- Spherical Mirrors
- A bacterial flagellum is composed of
- JIPMER - 2021
- Prokaryotic Cells
- $2,4-DNP $ test can be used to identify :
- JIPMER - 2021
- Chemical Reactions
- How many moles of acidified $K_2Cr_2O_7$ is required to liberate $6$ moles of $I_2$ from an aqueous solution of $I^-$ ?
- JIPMER - 2020
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
Concepts Used:
Laws of Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics in physics is a branch that deals with heat, work and temperature, and their relation to energy, radiation and physical properties of matter.
The First Law of Thermodynamics:
The first law of thermodynamics, also known as the Law of Conservation of Energy, states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; energy can only be transferred or changed from one form to another.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics:
The second law of thermodynamics says that the entropy of any isolated system always increases. Isolated systems spontaneously evolve towards thermal equilibrium—the state of maximum entropy of the system. More simply put: the entropy of the universe (the ultimate isolated system) only increases and never decreases.
The Third Law of Thermodynamics:
The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the temperature approaches absolute zero. The entropy of a system at absolute zero is typically zero, and in all cases is determined only by the number of different ground states it has. Specifically, the entropy of a pure crystalline substance (perfect order) at absolute zero temperature is zero



