Question:
If $f: R \rightarrow R$ is a differentiable function such that $f'(x)>2 f(x)$ for all $x \in R$, and $f(0)=1$, then
If $f: R \rightarrow R$ is a differentiable function such that $f'(x)>2 f(x)$ for all $x \in R$, and $f(0)=1$, then
Updated On: Jun 14, 2022
- $
- $
- $>
- $
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
$f'(x)-2 f(x)>0$
$\Rightarrow \frac{d}{d x}\left(f(x) \cdot e^{-2 x}\right)>0$
$\Rightarrow f(x) \cdot e^{-2 x}$ is increasing function
$\Rightarrow f(x) \cdot e^{-2 x}>f(0)=1 \,\,\,\,\forall x>0$
$f(x)>e^{2 x} \forall x>0$
$\Rightarrow f'(x)>2 f(x)>2 e^{2 x}>0 \forall x>0$
$\Rightarrow \frac{d}{d x}\left(f(x) \cdot e^{-2 x}\right)>0$
$\Rightarrow f(x) \cdot e^{-2 x}$ is increasing function
$\Rightarrow f(x) \cdot e^{-2 x}>f(0)=1 \,\,\,\,\forall x>0$
$f(x)>e^{2 x} \forall x>0$
$\Rightarrow f'(x)>2 f(x)>2 e^{2 x}>0 \forall x>0$
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Application of derivatives
- \(y=f(x)\) is a quadratic function passing through (–1, 0) and tangent to it at (1, 1) is \(y=x\). Find x intercept by normal at point (𝛂, 𝛂 + 1), (𝛂 > 0)
- JEE Main - 2023
- Mathematics
- Application of derivatives
Area of region enclosed by curve y=x3 and its tangent at (–1,–1)
- JEE Main - 2023
- Mathematics
- Application of derivatives
- Let $y=f(x)=\sin ^3\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\left(\cos \left(\frac{\pi}{3 \sqrt{2}}\left(-4 x^3+5 x^2+1\right)^{\frac{3}{2}}\right)\right)\right)$ Then, at $x=1$
- JEE Main - 2023
- Mathematics
- Application of derivatives
- Let $x=2$ be a local minima of the function $f(x)=2 x^4-18 x^2+8 x+12$, $x \in(-4,4)$ If $M$ is local maximum value of the function $f$ in $(-4,4)$, then $M =$
- JEE Main - 2023
- Mathematics
- Application of derivatives
- Let $x=2$ be a local minima of the function $f(x)=2 x^4-18 x^2+8 x+12$, $x \in(-4,4)$ If $M$ is local maximum value of the function $f$ in $(-4,4)$, then $M =$
- JEE Main - 2023
- Mathematics
- Application of derivatives
View More Questions
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let \(S=\left\{\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 & c \\ 1 & a & d\\ 1 & b & e \end{pmatrix}:a,b,c,d,e\in\left\{0,1\right\}\ \text{and} |A|\in \left\{-1,1\right\}\right\}\), where |A| denotes the determinant of A. Then the number of elements in S is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Matrices
- A block of mass \(5 kg\) moves along the \(x-\)direction subject to the force \(F = (−20x + 10) N,\) with the value of \(x \) in metre. At time \(t = 0 s,\) it is at rest at position \(x = 1 m\). The position and momentum of the block at \(t = (\pi/4)\) s are
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Work-energy theorem
- Two equilateral-triangular prisms \(P_1 \)and \(P_2\) are kept with their sides parallel to each other, in vacuum, as shown in the figure. A light ray enters prism \(P_1\) at an angle of incidence 𝜃 such that the outgoing ray undergoes minimum deviation in prism \(P_2\). If the respective refractive indices of \(P_1\) and\( P_2\) are \(√ 3 /2\) and \(√3\), then \(\theta = sin{−1}[\sqrt \frac{ 3}{ 2} sin ( \frac{\pi}{B} )],\) where the value of \(\beta\) is ______.
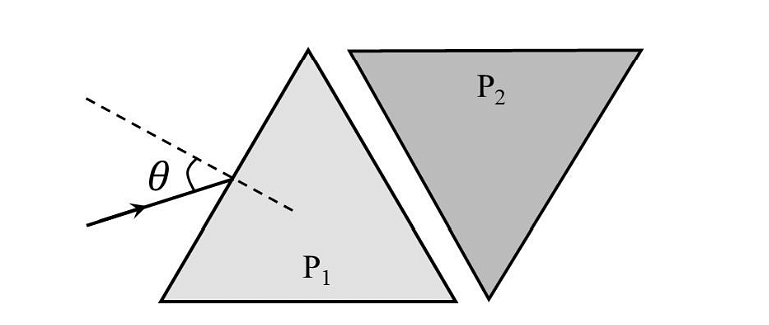
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- Let \(\overrightarrow{OP}=\frac{\alpha-1}{\alpha}\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\hat{k},\overrightarrow{OQ}=\hat{i}+\frac{\beta-1}{\beta}\hat{j}+\hat{k}\) and \(\overrightarrow{OR}=\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\frac{1}{2}\hat{k}\) be three vector where α, β ∈ R - {0} and 0 denotes the origin. If \((\overrightarrow{OP}\times\overrightarrow{OQ}).\overrightarrow{OR}=0\) and the point (α, β, 2) lies on the plane 3x + 3y - z + l = 0, then the value of l is _______.
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- Let \(\vec{p}=2\hat{i}+\hat{j}+3\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{q}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}\). If for some real numbers α, β and γ we have
\(15\hat{i}+10\hat{j}+6\hat{k}=α(2\vec{p}+\vec{q})+β(\vec{p}-2\vec{q})+γ(\vec{p}\times\vec{q})\),
then the value of γ is ________.- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Vector Algebra
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Application of Derivatives
Various Applications of Derivatives-
Rate of Change of Quantities:
If some other quantity ‘y’ causes some change in a quantity of surely ‘x’, in view of the fact that an equation of the form y = f(x) gets consistently pleased, i.e, ‘y’ is a function of ‘x’ then the rate of change of ‘y’ related to ‘x’ is to be given by
\(\frac{\triangle y}{\triangle x}=\frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}\)
This is also known to be as the Average Rate of Change.
Increasing and Decreasing Function:
Consider y = f(x) be a differentiable function (whose derivative exists at all points in the domain) in an interval x = (a,b).
- If for any two points x1 and x2 in the interval x such a manner that x1 < x2, there holds an inequality f(x1) ≤ f(x2); then the function f(x) is known as increasing in this interval.
- Likewise, if for any two points x1 and x2 in the interval x such a manner that x1 < x2, there holds an inequality f(x1) ≥ f(x2); then the function f(x) is known as decreasing in this interval.
- The functions are commonly known as strictly increasing or decreasing functions, given the inequalities are strict: f(x1) < f(x2) for strictly increasing and f(x1) > f(x2) for strictly decreasing.
Read More: Application of Derivatives



