If a rhombus has area 12 sq cm and side length 5 cm, then the length, in cm, of its longer diagonal is
\(\frac{\sqrt{37}+\sqrt{13}}{2}\)
\(\frac{\sqrt{13}+\sqrt{12}}{2}\)
\(\sqrt{(37)} + \sqrt{(13)}\)
\(\sqrt{(13)} + \sqrt{(12)}\)
The Correct Option is C
Approach Solution - 1
Let's designate the length of the longer diagonal of the rhombus as '2a' and the length of the shorter diagonal as '2b.'
The area of the rhombus is equal to 12 square centimeters, which can be expressed as:
\((\frac{1}{2}) \cdot (2a) \cdot (2b) = 12\) sq cm.
This simplifies to:
ab = 6.
The side length of the rhombus is 5 cm. Therefore,
a² + b² = 25.
Now, we can use the above equations to find the values of 'a' and 'b':
(a + b)² = a² + b² + 2ab
(a + b)² = 25 + 2(6) = 37
\(a + b = \sqrt{(37)}\) (equation 1).
Similarly,
(a - b)² = a² + b² - 2ab
(a - b)² = 25 - 2(6) = 13
\(a - b = \sqrt{(13)}\) (equation 2).
By solving equations 1 and 2, we can determine that the length of the long diagonal is 2a and is equal to:
\(2a=\sqrt{(37)} + \sqrt{(13)}.\)
Approach Solution -2
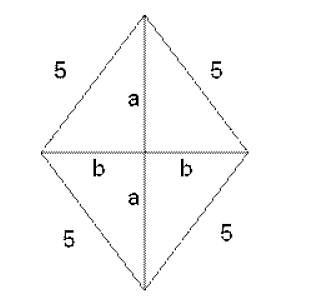
Let's assume that the rhombus's longer and shorter diagonals are, respectively, "2a" and "2b" in length.
12 sq cm is the rhombus's area.
\(12 \text{ sq cm} = \frac{1}{2} \times 2a \times 2b\)
ab is equal to 6.
The rhombus's side measures 5 cm.
Consequently, \(a^2 + b^2 = 25.\)
\((a + b)^2 = a^2 + b^2 + 2ab\)
\((a + b)^2 = 25 + 2(6) = 37\)
\(a + b = \sqrt{37} \quad \text{(eq. 1)}\)
\((a - b)^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab\)
\((a - b)^2 = 25 - 2(6) = 13 \)
\(a - b = \sqrt{13} \quad \text{(eq. 2)}\)
Solving equations (1) and (2) yields
Diagonal length = \(2a = \sqrt{37} + \sqrt{13}\)
Top Questions on Geometry
- Consider a right-angled triangle ABC, right angled at B. Two circles, each of radius r, are drawn inside the triangle in such a way that one of them touches AB and BC, while the other one touches AC and BC. The two circles also touch each other (see the image below).
If AB = 18 cm and BC = 24 cm, then find the value of r.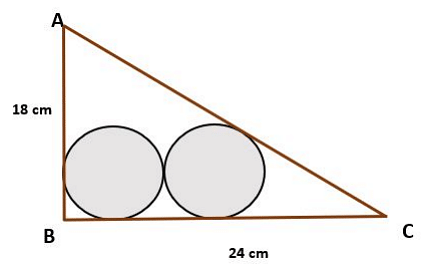
- A group of boys is practising football in a rectangular ground. Raju and Ratan are standing at the two opposite mid-points of the two shorter sides. Raju has the ball, who passes it to Rivu, who is standing somewhere on one of the longer sides. Rivu holds the ball for 3 seconds and passes it to Ratan. Ratan holds the ball for 2 seconds and passes it back to Raju. The path of the ball from Raju to Rivu makes a right angle with the path of the ball from Rivu to Ratan. The speed of the ball, whenever passed, is always 10 metre per second, and the ball always moves on straight lines along the ground.
Consider the following two additional pieces of information:
I. The dimension of the ground is 80 metres × 50 metres.
II. The area of the triangle formed by Raju, Rivu and Ratan is 1000 square metres.
Consider the problem of computing the following: how many seconds does it take for Raju to get the ball back since he passed it to Rivu? Choose the correct option. - A farmer has a triangular plot of land. One side of the plot, henceforth called the base, is 300 feet long and the other two sides are equal. The perpendicular distance, from the corner of the plot, where the two equal sides meet, to the base, is 200 feet.
To counter the adverse effect of climate change, the farmer wants to dig a circular pond. He plans that half of the circular area will be inside the triangular plot and the other half will be outside, which he will purchase at the market rate from his neighbour. The diameter of the circular plot is entirely contained in the base and the circumference of the pond touches the two equal sides of the triangle from inside.
If the market rate per square feet of land is Rs. 1400, how much does the farmer must pay to buy the land from his neighbour for the pond? (Choose the closest option.) - Given below are two statements
Statement I =If two chords XY and ZT of a circle intersects internally at point P,then PX-PYPZ-PT
Statement II =If two chords XY and ZT of a circle intersect internally at point P,then PXZ and PTY are similar triangles
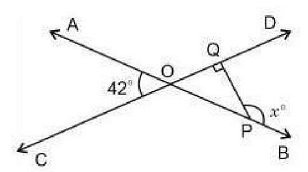
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below - In the figure, ∠AOC = 42° and PQ is perpendicular to CD. Find the value of x.
Questions Asked in CAT exam
- If x and y are real numbers such that x2 + (x-2y-1)2 = 4y(x+y), here the value x-2y is?
- CAT - 2023
- Linear & Quadratic Equations
- The number of coins collected per week by two coin-collectors A and B are in the ratio 3 : 4. If the total number of coins collected by A in 5 weeks is a multiple of 7, and the total number of coins collected by B in 3 weeks is a multiple of 24, then the minimum possible number of coins collected by A in one week is
- CAT - 2023
- Ratio and Proportion
- Anil borrows Rs 2 lakhs at an interest rate of 8% per annum, compounded half-yearly. He repays Rs 10320 at the end of the first year and closes the loan by paying the outstanding amount at the end of the third year. Then, the total interest, in rupees, paid over the three years is nearest to
- CAT - 2023
- SI & CI
- A fruit seller has a stock of mangoes, bananas and apples with at least one fruit of each type. At the beginning of a day, the number of mangoes make up 40% of his stock. That day, he sells half of the mangoes, 96 bananas and 40% of the apples. At the end of the day, he ends up selling 50% of the fruits. The smallest possible total number of fruits in the stock at the beginning of the day is
- CAT - 2023
- Percentage
- Let \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) be the two distinct roots of the equation of 2x2-6x+k=0, such that (\(\alpha+\beta\)) and \(\alpha\beta\) are the distinct roots of the equation x2+px+p=0, then, the value of 8(k-p) ?
- CAT - 2023
- Linear & Quadratic Equations
CAT Notification
 CAT Registration 2024 Dates Out, Check Details HereJuly 28, 2024
CAT Registration 2024 Dates Out, Check Details HereJuly 28, 2024


