If A'= \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 4 \\ -1 & 2 \\ 0 &1 \end{bmatrix}\)\(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 2 & 1 \\ 1 &2 & 3\end{bmatrix}\) , then verify that
(i) \((A+B)'=A'+B' \)
(ii) \((A-B)'=A'-B'\)
(i) \((A+B)'=A'+B' \)
(ii) \((A-B)'=A'-B'\)
Solution and Explanation
(i) It is known that A=(A')'
Therefore, we have:
A= \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & -1 & 0 \\ 4 & 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\)
B'= \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 1 \\ 2 & 2 \\ 1 &3 \end{bmatrix}\)
\(A+B\) = \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & -1 & 0 \\ 4 & 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\) + \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 2 & 1 \\ 1 &2 & 3\end{bmatrix}\)= \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 1 & 1 \\ 5 & 4 & 4 \end{bmatrix}\)
\(\therefore (A+B)'=\) \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 5 \\ 1 & 4 \\ 1 &4 \end{bmatrix}\)
\(A'+B'=\) \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 4 \\ -1 & 2 \\ 0 &1 \end{bmatrix}\)+ \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 1 \\ 2 & 2 \\ 1 &3 \end{bmatrix}\)= \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 5 \\ 1 & 4 \\ 1 &4 \end{bmatrix}\)
Thus, we verified that:(A+B)'=A'+B'
(ii) \(A-B\)= \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & -1 & 0 \\ 4 & 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\)- \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 2 & 1 \\ 1 &2 & 3\end{bmatrix}\) = \(\begin{bmatrix} 4 & -3 & -1 \\ 3 &0 & -2\end{bmatrix}\)
so\( (A-B)'\) = \(\begin{bmatrix} -4 & 3 \\ -3 & 0 \\ -1 &-2 \end{bmatrix}\)
A'-B'= \(\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 4 \\ -1 & 2 \\ 0 &1 \end{bmatrix}\)- \(\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 1 \\ 2 & 2 \\ 1 &3 \end{bmatrix}\)= \(\begin{bmatrix} -4 & 3 \\ -3 & 0 \\ -1 &-2 \end{bmatrix}\)
Hence we verified that: \((A-B)'=A'-B'\)
Top Questions on Matrices
- Let
\(M=\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 \\ 2 & 0 & 0 & 0 & -4 \\ 0 & 2 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 2 & 0 & 3 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 2 & 2 \end{pmatrix}\)
If p(x) is the characteristic polynomial of M, then p(2) - 1 equals _________ - Consider the 4 × 4 matrix
\(M = \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}\)
If ai,j denotes the (i, j)th entry of M-1 , then a4,1 equals __________ (rounded off to two decimal places). - For a matrix M, let Rowspace(M) denote the linear span of the rows of M and Colspace(M) denote the linear span of the columns of M. Which of the following hold(s) for all A, B, C ∈ M10(\(\R\)) satisfying A = BC ?
- Let \(a=\begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{\sqrt3} \\ \frac{-1}{\sqrt2} \\ \frac{1}{\sqrt6} \\ 0\end{bmatrix}\). Consider the following two statements.
P : The matrix I4 - aaT is invertible.
Q: The matrix I4 - 2aaT is invertible.
Then, which one of the following holds ? - Let A be a 6 × 5 matrix with entries in ℝ and B be a 5 × 4 matrix with entries in ℝ. Consider the following two statements.
P : For all such nonzero matrices A and B, there is a nonzero matrix Z such that AZB is the 6 × 4 zero matrix.
Q : For all such nonzero matrices A and B, there is a nonzero matrix Y such that BYA is the 5 × 5 zero matrix.
Which one of the following holds ?
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
What is the Planning Process?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2023
- Planning process steps
Evaluate \(\begin{vmatrix} cos\alpha cos\beta &cos\alpha sin\beta &-sin\alpha \\ -sin\beta&cos\beta &0 \\ sin\alpha cos\beta&sin\alpha\sin\beta &cos\alpha \end{vmatrix}\)
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2021
- Determinants
- Find the vector and the cartesian equations of the lines that pass through the origin and(5,-2,3).
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2021
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- A series LCR circuit with R = 20 W, L = 1.5 H and C = 35 μF is connected to a variable-frequency 200 V ac supply. When the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit, what is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle?
- CBSE CLASS XII
- Alternating Current
- A convex lens of glass is immersed in water compared to its power in air, its power in water will
- CBSE CLASS XII
- Spherical Mirrors
Concepts Used:
Transpose of a Matrix
The matrix acquired by interchanging the rows and columns of the parent matrix is called the Transpose matrix. The transpose matrix is also defined as - “A Matrix which is formed by transposing all the rows of a given matrix into columns and vice-versa.”
The transpose matrix of A is represented by A’. It can be better understood by the given example:

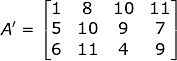
Now, in Matrix A, the number of rows was 4 and the number of columns was 3 but, on taking the transpose of A we acquired A’ having 3 rows and 4 columns. Consequently, the vertical Matrix gets converted into Horizontal Matrix.
Hence, we can say if the matrix before transposing was a vertical matrix, it will be transposed to a horizontal matrix and vice-versa.
Read More: Transpose of a Matrix



