Family Fabaceae differs from Solanaceae and Liliaceae. With respect to the stamens, pick out the characteristics specific to family Fabaceae but not found in Solanaceae or Liliaceae.
Family Fabaceae differs from Solanaceae and Liliaceae. With respect to the stamens, pick out the characteristics specific to family Fabaceae but not found in Solanaceae or Liliaceae.
Polyadelphous and epipetalous stamens
Monadelphous and Monothecous anthers
Epiphyllous and Dithecous anthers
Diadelphous and Dithecous anthers
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
In the family Fabaceae, the stamens are typically arranged in two groups (diadelphous) and each stamen has two distinct chambers (dithecous) in the anther. This arrangement is not present in Solanaceae or Liliaceae.
To provide a bit more context:
Polyadelphous and epipetalous stamens: This characteristic refers to stamens that are fused into several groups, and they are attached to the petals. This is not a specific characteristic of Fabaceae and can be found in some other plant families.
Monoadelphous and Monothecous anthers: This refers to stamens that are fused into a single group, and each stamen has a single chamber in the anther. This characteristic is not typical of Fabaceae.
Epiphyllous and Dithecous anthers: This refers to anthers that are attached to the surface of a leaf (epiphyllous) and have two chambers (dithecous). This characteristic is not specific to Fabaceae and is not present in Solanaceae or Liliaceae.
Diadelphous and Dithecous anthers: This is the correct characteristic for Fabaceae. It refers to stamens arranged in two groups and each stamen having two chambers in the anther. This arrangement is not found in Solanaceae or Liliaceae.
So, the correct option is (D): Diadelphous and Dithecous anthers
Top Questions on morphology of flowering plants
- Given below are two statements: One labelled as Assertion A and the other labelled as Reason R:
Assertion A: In gymnosperms the pollen grains are released from the microsporangium and carried by air currents.
Reason R: Air currents carry the pollen grains to the mouth of the archegonia where the male gametes are discharged and pollen tube is not formed.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Axile placentation is observed in
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
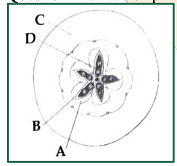
Which part of the fruit, labelled in the given figure makes it a false fruit?- NEET (UG) - 2022
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Identify the correct set of statements:
- The leaflets are modified into pointed hard thorns in Citrus and Bougainvillea
- Axillary buds form slender and spirally coiled tendrils in cucumber and pumpkin
- Stem is flattened and fleshy on Opuntia and modified to perform the function of leaves
- Rhizophora shows vertically upward growing roots that help to get oxygen for respiration
- Subaerially growing stems in grasses and strawberry help in vegetative propagation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- NEET (UG) - 2022
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
The flowers are Zygomorphic in:
- Mustard
- Gulmohar
- Cassia
- Datura
- Chilli
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- NEET (UG) - 2022
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- A metallic bar of Young’s modulus, 0.5 × 1011 N m–2 and coefficient of linear thermal expansion 10–5 °C–1, length 1 m and area of cross-section 10–3 m2 is heated from 0°C to 100°C without expansion or bending. The compressive force developed in it is :
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Youngs double slit experiment
- The E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is more positive than that of Cr3+/Cr2+ or Fe3+/Fe2+ due to change of
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Electronic configuration of atoms and ions
- A light ray enters through a right angled prism at point P with the angle of incidence 30° as shown in figure. It travels through the prism parallel to its base BC and emerges along the face AC. The refractive index of the prism is :
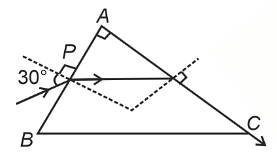
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Refraction Through A Prism
- \(^{290}_{82}X\stackrel{\alpha}{\rightarrow}Y\stackrel{e^+}{\rightarrow}Z\stackrel{\beta^-}{\rightarrow}P\stackrel{e^-}{\rightarrow}Q\)
In the nuclear emission stated above, the mass number and atomic number of the product Q respectively, are :- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Nuclear physics
- A compound X contains 32% of A, 20% of B and remaining percentage of C. Then, the empirical formula of X is:
(Given atomic masses of A=64; B=40; C=32 u)- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Some basic concepts of chemistry
NEET Notification
 Jharkhand NEET UG 2024 Round 2 Choice Filling Extended, Apply Now!Sep 18, 2024
Jharkhand NEET UG 2024 Round 2 Choice Filling Extended, Apply Now!Sep 18, 2024Concepts Used:
Morphology of Flowering Plants
Morphology in flowering plants tells us that every plant has two systems such as a root system and a shoot system. The root system digs deep into the ground and structures a system of its own. On the other hand, the shoot system is the one that is above ground level and includes various plant parts.
Root System
The descending part of the plant grows under the soil roots. During the germination process, the radicle from the seed grows earthward and branches out. The branches along with the primary root are called the root system. Roots lack chlorophyll and therefore they are not green in color. Roots are positively geotropic and hydrotropic, that is, they grow downwards ground and water, and negatively phototropic, which is growing away from light.
There are three types of root systems found in plants are as follows:
- TapRoot System
- Fibrous Root System
- Adventitious Root System
Shoot System
The stem is also an essential element of the plant. It is the ascending portion of the plant axis that bears branches, flowers, leaves, and fruits, as well as aiding in water and mineral conduction. It is the plant's aerial portion, brought about from an embryo's plumule or germinating seeds. Young stems are ordinarily green, but they finally turn woody and brown.



