Dry indehiscent single-seeded fruits formed from bicarpellary syncarpous inferior ovary is
- Berry
- Cremocarp
- Cypsela
- Caryopsis
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on morphology of flowering plants
- Given below are two statements: One labelled as Assertion A and the other labelled as Reason R:
Assertion A: In gymnosperms the pollen grains are released from the microsporangium and carried by air currents.
Reason R: Air currents carry the pollen grains to the mouth of the archegonia where the male gametes are discharged and pollen tube is not formed.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Axile placentation is observed in
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Family Fabaceae differs from Solanaceae and Liliaceae. With respect to the stamens, pick out the characteristics specific to family Fabaceae but not found in Solanaceae or Liliaceae.
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Identify the correct set of statements:
- The leaflets are modified into pointed hard thorns in Citrus and Bougainvillea
- Axillary buds form slender and spirally coiled tendrils in cucumber and pumpkin
- Stem is flattened and fleshy on Opuntia and modified to perform the function of leaves
- Rhizophora shows vertically upward growing roots that help to get oxygen for respiration
- Subaerially growing stems in grasses and strawberry help in vegetative propagation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- NEET (UG) - 2022
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
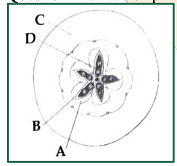
Which part of the fruit, labelled in the given figure makes it a false fruit?- NEET (UG) - 2022
- Biology
- morphology of flowering plants
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- A thin flat circular disc of radius 4.5 cm is placed gently over the surface of water. If surface tension of water is 0.07 Nm-1, then the excess force required to take it away from the surface is :
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Surface tension
- Which of the following are required for the dark reaction of photosynthesis?
A. Light
B. Chlorophyll
C. CO2
D. ATP
E. NADPH
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?
- If \(x=5\sin(\pi i+\frac{\pi}{3})m\) represents the motion of a particle executing simple harmonic motion, the amplitude and time period of motion, respectively, are :
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- simple harmonic motion
- The highest number of helium atoms is in
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Electronic configuration of atoms and ions
- \(^{290}_{82}X\stackrel{\alpha}{\rightarrow}Y\stackrel{e^+}{\rightarrow}Z\stackrel{\beta^-}{\rightarrow}P\stackrel{e^-}{\rightarrow}Q\)
In the nuclear emission stated above, the mass number and atomic number of the product Q respectively, are :- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Nuclear physics
Concepts Used:
Morphology of Flowering Plants
Morphology in flowering plants tells us that every plant has two systems such as a root system and a shoot system. The root system digs deep into the ground and structures a system of its own. On the other hand, the shoot system is the one that is above ground level and includes various plant parts.
Root System
The descending part of the plant grows under the soil roots. During the germination process, the radicle from the seed grows earthward and branches out. The branches along with the primary root are called the root system. Roots lack chlorophyll and therefore they are not green in color. Roots are positively geotropic and hydrotropic, that is, they grow downwards ground and water, and negatively phototropic, which is growing away from light.
There are three types of root systems found in plants are as follows:
- TapRoot System
- Fibrous Root System
- Adventitious Root System
Shoot System
The stem is also an essential element of the plant. It is the ascending portion of the plant axis that bears branches, flowers, leaves, and fruits, as well as aiding in water and mineral conduction. It is the plant's aerial portion, brought about from an embryo's plumule or germinating seeds. Young stems are ordinarily green, but they finally turn woody and brown.



