A metallic rod of mass per unit length $0.5 \, kg \, m^{-1}$ is lying horizontally on a smooth inclined plane which makes an angle of $30^{\circ}$ with the horizontal. The rod is not allowed to slide down by flowing a current through it when a magnetic field of induction $0.25 \,T$ is acting on it in the vertical direction. The current flowing in the rod to keep it stationary is
- 11.32 A
- 7.14 A
- 14.76 A
- 5.98 A
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
mg $\sin 30^{\circ}=I / B \cos 30^{\circ}$
$I =\frac{ mg }{l B } \,\tan 30^{\circ}$
$=\frac{0.5 \times 9.8}{0.25 \times \sqrt{3}} $
$=11.32\, A$
Top Questions on Moving charges and magnetism
- Two beads, each with charge q and mass m, are on a horizontal, frictionless, non-conducting, circular hoop of radius R. One of the beads is glued to the hoop at some point, while the other one performs small oscillations about its equilibrium position along the hoop. The square of the angular frequency of the small oscillations is given by [ \(\epsilon_0 \)is the permittivity of free space.]
- JEE Advanced - 2024
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
- A freely suspended needle of a magnetic compass comes to rest along the geographic
- AP POLYCET - 2024
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
- Two charged particles, having same kinetic energy, are allowed to pass through a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of motion If the ratio of radii of their circular paths is $6: 5$ and their respective masses ratio is $9: 4$ Then, the ratio of their charges will be :
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
- In a moving coil galvanometer if the number of turns increases by 25%, then change in voltage sensitivity is?
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
- An electron with energy $01\, keV$ moves at right angle to the earth's magnetic field of $1 \times 10^{-4} Wbm ^{-2}$ The frequency of revolution of the electron will be (Take mass of electron $=90 \times 10^{-31} kg$ )
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Moving charges and magnetism
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- The current in a coil changes from 2A to 5A in 0.3s. The magnitude of emf induced in the coil is 1.0V. The value of self-inductance of the coil is
- KCET - 2023
- Electromagnetic induction
- A stretched wire of a material whose Young's modulus Y = 2 × 1011 Nm-2 has Poisson's ratio of 0.25. Its lateral strain εl = 10-3. The elastic energy density of the wire is
- KCET - 2023
- mechanical properties of solids
- A particle moves along the curve \(\frac{x^2}{16}+\frac{y^2}{4}=1\). When the rate of change of abscissa is 4 times that of its ordinate, then the quadrant in which the particle lies is
- KCET - 2023
- Conic sections
- A point object is moving at a constant speed of 1 ms-1 along the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 10cm. The speed of the image is also 1 ms-1 , when the object is at _______ cm from the optic centre of the lens.
- KCET - 2023
- spherical lenses
- A cubical Gaussian surface has side of length a = 10 cm. Electric field lines are parallel to x-axis as shown. The magnitudes of electric fields through surfaces ABCD and EFGH are 6kNC-1 and 9kNC-1 respectively. Then the total charge enclosed by the cube is
[Take ε0 = 9 × 10-12 Fm-1]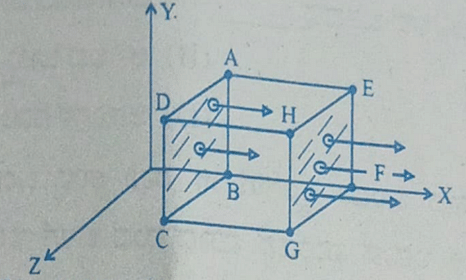
- KCET - 2023
- Gauss Law
NEET Notification
 Jharkhand NEET UG 2024 Round 2 Choice Filling Extended, Apply Now!Sep 18, 2024
Jharkhand NEET UG 2024 Round 2 Choice Filling Extended, Apply Now!Sep 18, 2024Concepts Used:
Moving Charges and Magnetism
Moving charges generate an electric field and the rate of flow of charge is known as current. This is the basic concept in Electrostatics. Another important concept related to moving electric charges is the magnetic effect of current. Magnetism is caused by the current.
Magnetism:
- The relationship between a Moving Charge and Magnetism is that Magnetism is produced by the movement of charges.
- And Magnetism is a property that is displayed by Magnets and produced by moving charges, which results in objects being attracted or pushed away.
Magnetic Field:
Region in space around a magnet where the Magnet has its Magnetic effect is called the Magnetic field of the Magnet. Let us suppose that there is a point charge q (moving with a velocity v and, located at r at a given time t) in presence of both the electric field E (r) and the magnetic field B (r). The force on an electric charge q due to both of them can be written as,
F = q [ E (r) + v × B (r)] ≡ EElectric +Fmagnetic
This force was based on the extensive experiments of Ampere and others. It is called the Lorentz force.



