
Content Strategy Manager
The general amino acid structure is given by NH2-CRH-COOH, where R is the side chain.
- Amino acids can be defined as the compound containing carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen.
- They are the monomers of proteins synthesized in the body.
- In the structure of amino acid, both the amino and the carboxylate groups are attached to the same alpha carbon.
- The R group can change based on the type of amino acid.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Amino acid, nitrogen, carbon, amino group, carboxylate group, proteins
What is an amino acid?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Amino acids are carbon compounds that act as a monomer for the synthesis of protein. They have both an amino group and a carboxylate group. This is the reason they can act as a base and an acid.
- There are a total of 20 amino acids.
- Of these, there are 9 essential and 11 non-essential amino acids.
- Essential amino acids are those that cannot be synthesized in the body and needs to be taken through diet.
- Non-essential amino acids are synthesized by the body.
Read more: Difference between essential and non-essential amino acids
Structure of amino acids
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The structure of an amino acid can be given by NH2-CRH-COOH, Here R can change depending on the amino acids. The simplest amino acid is glycine, it has an R group as hydrogen. All α amino acids have the same general structure, except proline. Proline is an imino acid that has a secondary amino group. (-NH-).
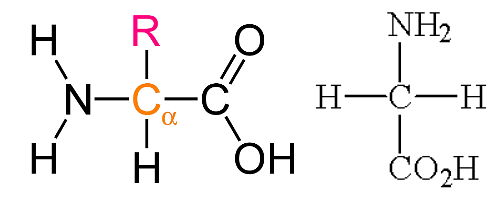
General structure Glycine
Read more: Peptide Bond
Types of amino acids
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are four types of amino acids based on the R group attached. They are as follows:
- Non-polar and neutral
- Polar and neutral
- Acidic and polar
- Basic and polar
Non-Polar and Neutral
The amino acids with nonpolar side chains are Glycine, valine, alanine, leucine, isoleucine, proline, methionine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan. The structure for the same are as follows:
| Amino acid | Structure |
|---|---|
| Glycine: Glycine is the simplest amino acid. It acts as a precursor of proteins, collagen has 35% of glycine. Glycine can be coded by all codons that start with GG. Glycine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. |  |
| Valine: valine is an alpha amino acid. It is coded by all codons that start with GU. The synthesis of valine takes place in plants and not in animals. Low levels of valine can lead to insulin resistance and weight loss. |  |
| Alanine: The L isomers of alanine are incorporated into the proteins. They are coded by all codons that start with GC. In mammals, the glucose alanine cycle is regulated by alanine. Changes in the alanine cycle can induce the chance of type II diabetes. |  |
| Leucine: It is a branched amino acid, the primary metabolic end products are acetyl CoA and acetoacetate. Leucine tends to slow the process of degradation of muscle tissues as it increases the synthesis of muscle proteins. |  |
| Isoleucine: It is a non-polar uncharged amino acid. It can be synthesised by threonine and methionine in plants. It is coded by AUU, AUC and AUA. High levels of isoleucine causes insulin resistance.It also helps in the functioning of fetal haemoglobin. |  |
| Proline: Proline is a secondary amine. It is a non essential amino acid that are derived from L-glutamate. |  |
| Methionine |  |
| Phenylalanine |  |
| Tryptophan |  |
Polar and neutral
The examples of amino acids with polar and neutral charge are serine, threonine, cysteine, asparagine, glutamine, and tyrosine. Of these, there are three amino acids that have hydroxyl groups (Serine, threonine, and tyrosine).
Acidic and Polar amino acids
The examples of acidic and polar amino acids are: Aspartate and Glutamate

Glutamate

Aspartate
Basic and Polar amino acids
The amino acids containing basic groups are: Lysine, Arginine and histidine
| Amino acid | Structure |
|---|---|
| Lysine |  |
| Arginine |  |
| Histidine |  |
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rancidity | Important Notes on Sucrose | Carbohydrates |
| Vitamins | Maltose | Nucleic Acids |
Things to Remember
- Amino acids are carbon compounds that are the monomers of proteins.
- Two amino acids are joined together with the help of a peptide bond to form a protein.
- The general structure of amino acids is NH2-CHR-COOH. Glycine is the simplest amino acid with the R group as Hydrogen.
- There are four types of amino acids: Non-polar and neutral, Polar and neutral, Acidic and polar, and Basic and polar
- Amino acids can also be divided into essential and non-essential amino acids.
- There are three amino acids that have hydroxyl groups. (serine, threonine and tyrosine)
- Methionine and cysteine are amino acids that have sulphur group present
Previous Year Questions
- Extraction of metal from the ore cassiterite involves...[JEE Advanced 2011]
- Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are...[NEET UG 2014]
- Interfascicular cambium and cork cambium are formed due to..
- Pneumotaxic centre is present in...[UP CPMT 2007]
- Reaction of HBr with propene in the presence of peroxide gives….[NEET UG 2004]
- Assuming the expression for the pressure exerted by the gas on the walls of the container, it can be shown that pressure is...[MHT CET 2016]
- Which among the following is the strongest acid?...[TS EAMCET 2017]
- Isopropyl alcohol on oxidation forms..
- A vector is not changed if..
- Which of the following arrangements does not represent the correct order of the property stated against it?...[JEE Main 2013]
Sample Questions
Ques: What are amino acids? (2 marks)
Ans: Amino acids are carbon compounds. They are 20 in number and act as the monomer of proteins. They can be divided into essential and nonessential amino acids. Essential amino acids need to be taken through diet as they cannot be synthesised by the body. On the other hand, our body is capable of making non-essential amino acids. The general structure of amino acid is NH2-CHR-COOH.
Ques: Draw the structure of Polar and neutral amino acids. (5 marks)
Ans:
| Amino acids | Structure |
|---|---|
| Serine |  |
| Threonine |  |
| Tyrosine |  |
| Asparagine |  |
| Glutamine |  |
| Cysteine |  |
Ques: What are the types of amino acids? (2 marks)
Ans: Apart from diving the amino acids as essential and non-essential. The types of amino acids are as follows:
- Non-polar and neutral: example- Glycine, valine, alanine, leucine
- Polar and neutral: Example- serine, threonine
- Acidic and polar: Example- Aspartate and Glutamate
- Basic and polar: Example- Lysine, Arginine, and histidine
Ques: Name the amino acids that have sulfur and draw structure. (3 marks)
Ans: There are two amino acids that are sulphur-containing. They are methionine and cysteine.
| Amino acid | Structure |
|---|---|
| Cysteine |  |
| Methionine |  |
Ques: What is the difference between essential and non-essential amino acids? (3 marks)
Ans:
| Essential amino acids | Nonessential amino acids |
|---|---|
| They are also called indispensable amino acids. | They are also called dispensable amino acids. |
| They cannot be synthesized by the body. | Our body can synthesize these amino acids |
| They must be obtained from the diet | They are not required through diet |
| There are 9 such amino acids | There are 11 such amino acids |
| Example: Histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, valine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine | Example: alanine, cysteine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine, proline, serine, and tyrosine |
Ques: Draw the structure of amino acid with a hydroxyl group. (3 marks)
Ans: The amino acids with hydroxyl group are as follows:
| Amino acid | Structure |
|---|---|
| Serine |  |
| Threonine |  |
| Tyrosine |  |
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments