
Content Writer
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
- An object can accelerate only if it changes its speed or direction or both.
- The change in the velocity could be an increase or decrease in speed or a change in the direction of motion.
- It is a vector quantity as it has both magnitude and direction.
- The SI unit of acceleration is m/s2.
Acceleration is calculated as the change in velocity divided by the total time taken. Acceleration Formula is given as
| \(Acceleration = {Change\, in \,Velocity \over Time\,Taken}\) |
Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Motion in a Straight Line
Key Terms: Acceleration, Velocity, Displacement, Distance, Motion, Speed, Acceleration Formula, Vector, Equations of Motion
What is Acceleration?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
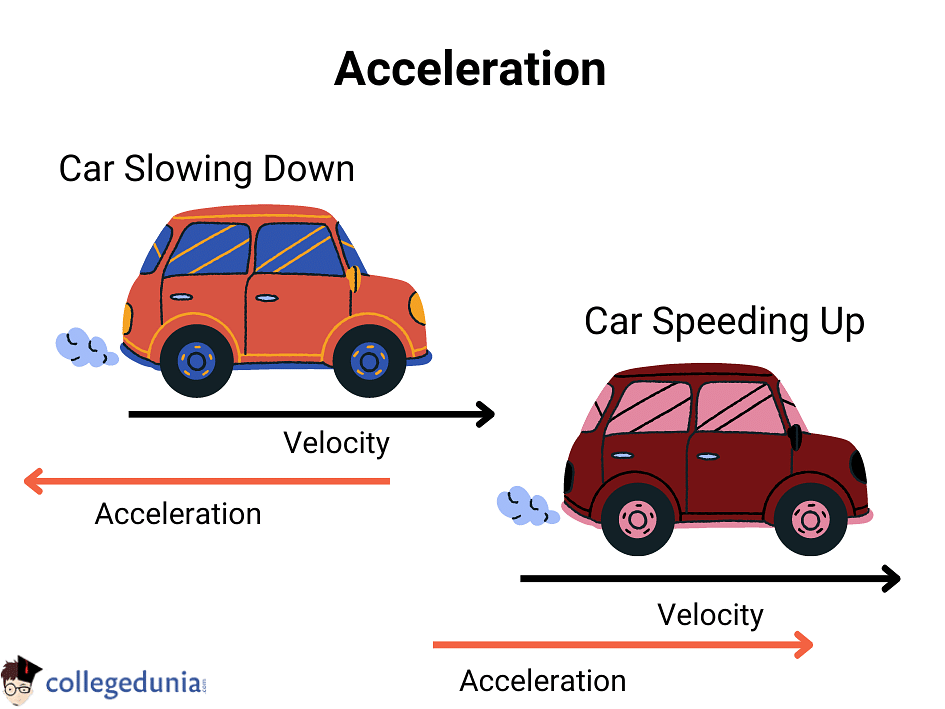
Acceleration is the rate at which the velocity of an object changes with time. A body accelerated if it either changes its speed or direction or both.
- Acceleration is denoted by ‘a’ and its SI unit is m/s2.
- Acceleration has both magnitude and direction, thus, it is a vector quantity.
- It is the change in the velocity divided by the time interval.
- It is the second derivative of position with respect to time.
- It is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time.
- When an object’s velocity and acceleration are in the same direction, the object speeds up.
- When the velocity and acceleration are in opposite directions, the object slows down.
Read More:
Acceleration Formula
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. Acceleration Formula is given as
\(Acceleration = {Change\, in \,Velocity \over Time\,Taken}\)
| \(a = {V_f \, -\,V_i \over t}\) |
Where
- a is the Acceleration (m/s2).
- vf is the Final Velocity (m/s).
- vi is the Initial Velocity (m/s).
- t is the Time Interval (s).
According to the three equations of motion, Acceleration Formula is given as follows:
v = u + at
v2 = u2 + 2as
s = ut + ½ at2
Where
- u: Initial Velocity
- v: Final Velocity
- t: Time Taken
- a: Acceleration
- s: Distance/Displacement
Read More: Average Acceleration Formula

Acceleration
Solved Examples on Acceleration Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
To understand the concept of the Acceleration Formula better, a few examples are illustrated below.
Example 1: Calculate the acceleration if a toy bus accelerates from 2 m/s to 5 m/s in 5 s.
Solution: Given that
- Initial Velocity u = 2 m/s
- Final Velocity v = 5 m/s
- Time Taken t = 5 s
Using the Acceleration Formula,
\(a = {v\,-\,u \over t}\)
a = (5 – 2)/5
a = 3/5
a = 0.6 m/s2
Thus, the acceleration of the toy bus is 0.6 m/s2.
Example 2: A car starts from rest and achieves a speed of 72 km/h in 5 seconds. Find its acceleration.
Solution: It is given that,
- u = 0
- v = 72 km/h = 20 m/s
- t = 5 s
Using the Acceleration Formula,
\(a = {v\,-\,u \over t}\)
a = (20 – 0)/4
a = 5 m/s2.
Thus, the acceleration of the car is 5 m/s2.
Read More: Motion in a Straight Line Important Questions
Example 3: A car is moving at a speed of 108 km/h and slows down to 72 km/h in 5 s. What will be the acceleration of the car?
Ans. Given that
- Initial velocity (u) = 108 km/h = 30 m/s
- Final velocity (v) = 72 km/h = 20 m/s
- Time Taken (t) = 5 sec
Using the Acceleration Formula,
\(a = {v\,-\,u \over t}\)
a = (20-30)/5
a = -10/5 = -2 m/s2
Thus, the acceleration (retardation) of the car is -2 m/s2.
Dimensional Formula of Acceleration
[Click Here for Previous Years’ Questions]
The unit of acceleration is m/sec2. Thus, the dimensional formula of acceleration is given as:
| M0 L1 T-2 |
Where
- M: Mass
- L: Length
- T: Time
Check More:
Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 Handwritten Notes
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
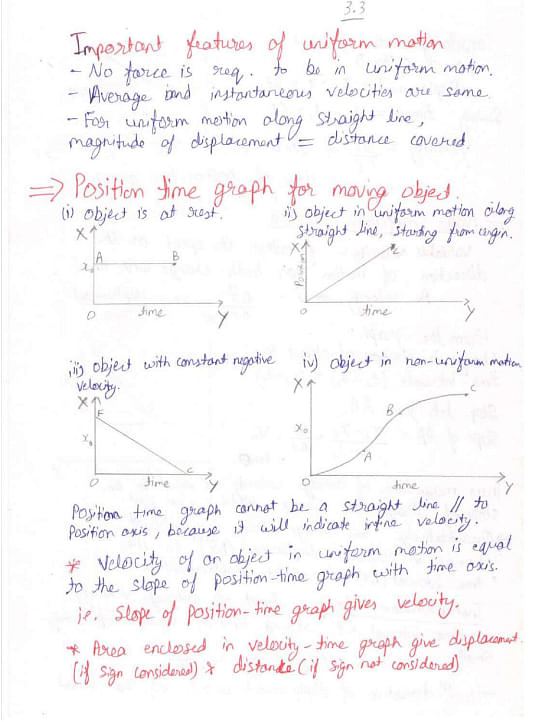
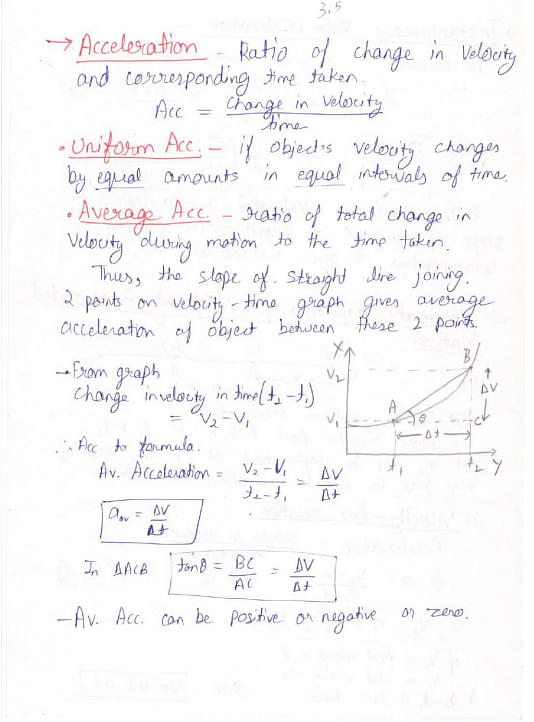
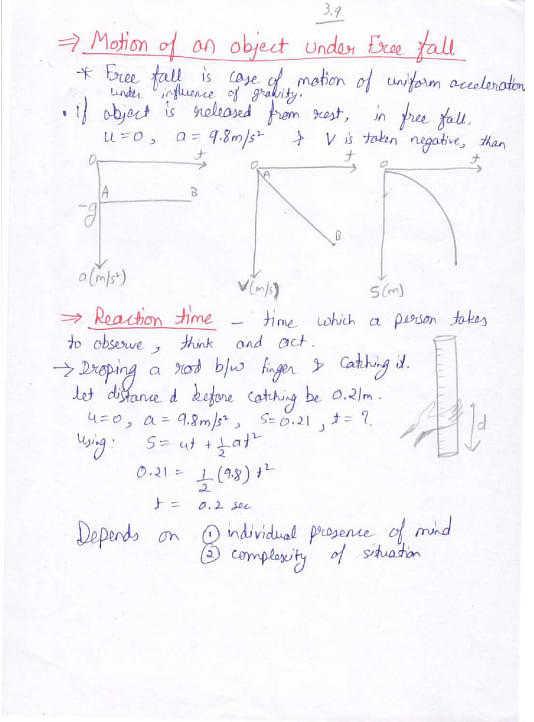
Here are the handwritten notes on Class 11 Motion in a Straight Line:














Things to Remember
- Acceleration is defined as the rate at which the velocity of an object changes with time.
- Acceleration occurs when there is a change in the speed or direction of motion.
- It is a vector quantity and the SI unit of acceleration is m/s2.
- The dimensional formula of acceleration is M0 L1 T-2.
- Acceleration Formula is \(a = {v\,-\,u \over t}\), where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity and t is the time taken.
- Acceleration can be positive, negative, or zero.
Previous Years’ Questions
- From the top of a tower of two stones, whose masses are in the ratio… [BITSAT 2005]
- A bullet loses 1/20 of its velocity after penetrating a plank…
- A coin is placed on a horizontal platform which undergoes vertical simple… [AIIMS 2008]
- The velocity of bullet is reduced from 200m/s to 100m/s while travelling… [Haryana PMT 2004]
- The v−t graph of a moving object is given in figure… [Chhattisgarh PMT 2007]
- The displacement, velocity and acceleration in a simple harmonic motion… (JKCET 2013)
- The time period of oscillation of a simple pendulum is…
- Speeds of two identical cars are U and 4U at a specific instant…
- Stopping distance of a moving vehicle is directly proportional to…
- The area under the acceleration-time graph represents the…
- The acceleration of a moving body is found from the… (KEAM)
- The acceleration of any electron due to the… (BCECE 2010)
- The velocity-displacement graph of a particle is shown in the figure. Which...
Sample Questions
Ques. A bus accelerates from 3 m/s to 5 m/s in 5 s. What is its acceleration? (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that
- Initial Velocity u = 3 m/s
- Final Velocity v = 5m/s
- Time Taken t = 5s
Using the Acceleration Formula,
a = (v – u)/t
a = (5 – 3)/5
a = 2/5
a = 0.4 m/s2
Therefore, the acceleration of the bus is 0.4 m/s2.
Ques. A stone is thrown into the river from a bridge. It takes 4s for the stone to touch the river’s water surface. Compute the height of the bridge from the water level. (3 Marks)
Ans. According to the question,
- Initial Velocity, u = 0
- Time Taken, t = 4s
- Acceleration due to Gravity, a = g = 9.8 m/s2
Distance traveled by stone = Height of bridge = s
Using the equation of motion,
s = ut + ½ at2
s = 2 x 9.8 = 19.6 m
Thus, the height of the bridge is 19.6 m.
Ques. What is the difference between Acceleration and Velocity? (3 Marks)
Ans. The difference between acceleration and velocity is as follows:
| Parameter | Acceleration | Velocity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acceleration is defined as the change in the velocity of an object with respect to time. | Velocity is defined as the speed of an object in a particular direction. |
| Formula | a = Velocity/Time | v = Displacement/Time |
| Unit | Its SI unit is m/s2. | Its SI unit is m/s. |
Ques. Define gravitational acceleration. (3 Marks)
Ans. Gravitational Acceleration is the acceleration an object experiences due to the force of gravity.
- It is used for indicating the intensity of the gravitational field.
- Gravitational Acceleration is expressed in the units of m/s2.
- The value of gravitational acceleration on the surface of the earth is 9.8 m/s2.
Ques. A car starts from rest and achieves a speed of 54 km/h in 3 seconds. Find its acceleration. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- u = 0
- v = 54 km/h = 15 m/s
- t = 3 s
a = (v – u)/t
a = (15 – 0)/3 = 5 m/s2.
Thus, the acceleration of the given car is 5 m/s2.
Ques. A car moves in a circular track with a constant velocity, Will it experience acceleration? (2 Marks)
Ans. The speed of the car is constant; however, the direction is continuously changing, which means the velocity is also changing. As there is a change in direction, the car will experience acceleration.
Ques. Define radial acceleration. (2 Marks)
Ans. When there is an acceleration of an object along the radius directed toward the center, it is known as radial acceleration. It is expressed as radian/sec2.
Ques. What will be the acceleration of an object which moves with uniform velocity? (2 Marks)
Ans. The acceleration of an object which is moving with a constant velocity will be zero as both the initial and final velocities will be equal to each other.
Ques. A boy is running at 7 m/s, and skids to a halt in 2 seconds. What will be the acceleration? (3 Marks)
Ans. It is given that,
- u = 7 m/s
- v = 0
- t = 2 s
Using the Acceleration Formula,
a = (v – u)/t
a = (0 – 7)/2
a = – 3.5 m/s2
Thus, the acceleration of the boy is – 3.5 m/s2.
Ques. Is acceleration a scaler or a vector quantity? (1 Mark)
Ans. Acceleration has both magnitude and direction, thus, it is a vector quantity.
Ques. A bike accelerates from 6 m/s to 10 m/s in 10 s. What will be its acceleration? (3 Marks)
Ans. It is given that,
- Initial Velocity (u) = 6 m/s
- Final Velocity (v) = 10 m/s
- Time Taken (t) = 10 s
Using the Acceleration Formula,
Acceleration a = (v – u) / t
a = (10 – 6) / 10
a = 0.4 m/s2
Thus, the acceleration of the bike is 0.4 m/s2.
Check-Out:





Comments