.jpg?h=35&w=35&mode=stretch)
Veda Burman Study Abroad Content Specialist
Study Abroad Content Specialist | Updated On - Jun 19, 2025
What's New?
19 June 2025: The US has resumed student visa interviews with one big change — mandatory social media checks. Applicants must list all personal social media accounts used in the past five years and set them to public. Visa officers will review online activity for any anti-American sentiment or concerning content. This rule applies to all F, M, and J visa applicants. Inactive and secondary accounts must also be disclosed.
29 May 2025: The US government has halted scheduling new international student visa interviews at consulates worldwide, as it prepares to expand its social media vetting process.
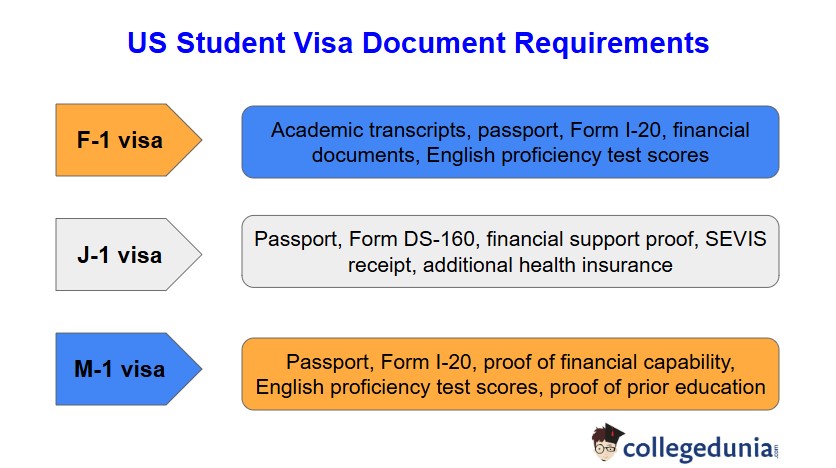
US student visa can be classified into F, J, and M categories. The F-1 visa is for academic students. It is the most popular visa status used by students in USA. The J-1 visa is for exchange visitors, and the M-1 visa is for vocational students. These visas can be subclassified like F-1, J-1, F-2, etc., depending on your status and relation with the main beneficiary.
The main visa holder can take a family member with them to the USA as a beneficiary. The F-2, J-2, and M-2 visas are for dependents corresponding to each of the F-1 visa, J-1 visa and M-1 visa holders, respectively. Check out the documents required to avail the various types of US student visa:
US Student Visa Types and Differences
US student visas can be classified into 3 main types, F visa, J visa and M visa. These visas can further be subclassified into F1, F2, J1, J2 and more depending on the status of the beneficiary. Here are some of the US student visa types and their characteristics:
| Visa Type | Purpose | Ideal for | Employment Options | Dependents |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-1 visa | Academic Studies | Students of colleges and universities in USA | Limited on- and off-campus work | F-2 (limited study options) |
| J-1 visa | Exchange Programs | Students in exchange programs with institutional/government funding | Requires permission from sponsor | J-2 (part-time/full-time study, some work options) |
| M-1 visa | Vocational/Technical Training | Students in non-academic programs | No employment allowed | M-2 (study allowed, no work) |
F-1 Visa: Academic Studies
The F-1 visa is the most popular US student visa, primarily for students enrolled in full-time academic or language programs. The details of F-1 visa are as follows:
F1 Visa Eligibility:
- Indian students must have a confirmed acceptance from a SEVP-enlisted US university.
- Proof of English proficiency through tests like TOEFL or IELTS. A TOEFL score above 90 or IELTS score above 6.5 is considered competitive.
- Proof of sufficient financial availability for the first year of study.
- Valid Form I-20, issued by the educational institution.
F1 Visa Dependents: F-2 dependents (spouses and children under 21) cannot work but can study part-time or participate in non-academic courses.
F1 Visa Employment Options:
- On-Campus: Indian students can pursue part-time employment of up to 20 hours per week without a special permit.
- Off-Campus: Requires authorization from the US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
- Practical Training: Eligible for Curricular Practical Training (CPT) during studies and Optional Practical Training (OPT) for up to 12 months post-graduation. Students pursuing STEM courses in USA may extend OPT by an additional 24 months.
Read More: OPT vs CPT
Pros and Cons of F Visa
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of F-1 student visa in USA:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Permits on-campus employment | Off-campus work requires USCIS approval |
| CPT and OPT opportunities available | Limited OPT duration, requiring re-application |
| Dependents may join as F-2 and study part-time | Dependents cannot work on an F-2 visa |
J-1 Visa: Exchange Programs
The J-1 visa caters to students participating in exchange programs, often supported by scholarships, and institutional, or government funding.
J1 Visa Eligibility:
- Indian students should participate in an exchange program in USA (e.g., Fulbright) to be eligible for a J-1 visa.
- For a J-1 visa, you should have proof of financial support covering the entire program duration. The majority funding of the exchange program in USA should be from non-personal sources (e.g., scholarships, government grants).
- Form DS-2019 issued by the sponsoring institution is mandatory for this visa.
- You should also comply with the health insurance requirements in USA to be eligible for J-1 visa.
Also Check: Health Insurance in USA
J-1 Visa Dependents: J-2 visas are issued for dependents of J-1 visa. J-2 dependents can study part-time or full-time and can also apply for work permits in USA. However, if J-1 students are part of a government-funded program, they may be subject to a Two-Year Home Country Physical Presence Requirement.
J-1 Visa Employment Options:
- Academic Training: The J-1 visa allows practical experience related to your field of study. It is available during or after studies for up to 18 months.
- J-2 Dependents: J-2 dependents are authorized to work only during the dates allowed on their EAD card. They can work both full-time and part time. However, any income earned through J-2 employment should not be used to support the J-1 visa holder. This income can be used for recreational purposes.
Pros and Cons of J Visa
A list of the benefits and drawbacks of J visa in USA is provided in the below table:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Academic Training for practical experience | Strict requirements for financial support |
| Dependents can work if approved | Two-Year Home Country Physical Presence Requirement for some students |
| Enables cultural and academic exchange | Limited to specific programs and funding structures |
M-1 Visa: Vocational Training
The M-1 visa is intended for students enrolled in non-academic, vocational programs, such as technical courses or short-term training programs.
M-1 Visa Eligibility:
- To get a M-1 visa, you should be enrolled in a SEVP-enlisted U.S. vocational or technical institution.
- You must show proof of adequate financial resources to cover the program and cost of living in USA.
- Commitment to non-immigration intent.
Supporting Documents for M-1 Visa:
- Form I-20 from the vocational school.
- Proficiency in English through exams like TOEFL or IELTS.
- Valid passport and proof of prior education qualifications.
M-1 Visa Dependents: The spouse or children of a M-1 visa beneficiary are eligible for M-2 visa in USA. M-2 dependents can study part-time in non-academic courses in USA but are not allowed to work.
M-1 Visa Employment Options:
- M-1 visa holders are not allowed to work in USA, be it on or off-campus.
- The M-1 visa is limited to Optional Practical Training (OPT) post-study for a specific duration.
Pros and Cons of M Visa
Check out the major pros and cons of M visa, tabulated below:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Allows vocational/technical studies | No employment opportunities during study |
| Suitable for short-term programs | Limited to non-academic institutions |
| Fixed program duration | Dependents cannot work on M-2 visa |
Know More: Post Study Work Visa in USA
F-1 visa is ideal for degree seeking college and university students in USA. The J-1 visa suits exchange-based programs with a majority of their financial support from sources other than personal funds. The M-1 visa is designed for technical and vocational training students.
FAQs
Ques. What are the main differences between various US student visas?
Ans. The F-1 visa in USA is for full-time academic studies at colleges or universities. The J-1 visa is suited for exchange programs funded by institutions or governments. The M-1 visa is intended for vocational or technical training programs. Each visa has unique employment, funding, and eligibility criteria.
Ques. Are there work opportunities for US student visa holders?
Ans. F-1 students in USA can work on-campus, part-time, and may engage in Optional Practical Training (OPT) and Curricular Practical Training (CPT) with authorization. J-1 visa holders can participate in Academic Training, related to their studies, with sponsor approval. M-1 visa holders have very limited work options and are only eligible for post-study OPT in specific cases.
Ques. Can dependents work or study under F-1, J-1, and M-1 visas?
Ans. F-2 dependents (spouses and children of F-1 holders) can study part-time in USA but cannot work. J-2 dependents (of J-1 holders) can study full-time or part-time and may apply for work authorization. M-2 dependents (of M-1 holders) can study part-time but are not allowed to work.
Ques. What is the 2-Year Home Country Physical Presence Requirement for J-1 visa holders?
Ans. Some J-1 visa holders, especially those on government-funded programs, must return to their home country for 2 years after completing their studies in USA. This requirement restricts visa extensions or changes until fulfilled, but can be waived in certain circumstances.





1691151352.png?tr=w-305,h-145,c-force?h=40&w=40&mode=stretch)
1715689273.png?tr=w-305,h-145,c-force?h=40&w=40&mode=stretch)









Comments