Tropism is the active growth or slow movement of plant as a reaction to exogenous stimuli. All living organisms have an inherent nature to either move away or towards an external stimulus. A stimulus is an object or an event whose outcome evokes some kind of movement.
- For example, kids grow up as adults.
- This growth (movement) is a result of the changes taking place in the body as a response to the food (stimulus) a person eats.
- The stimuli triggering growth movements could fall into a broad class of environmental factors such as light, water, touch, temperature changes, gravity, etc.
- Animals show tropic movements by physically moving around, however, plants respond by growth in their parts towards or away from the stimulus.
- This directional movement hence can be positive (towards stimulus) or negative (away from the stimulus).
| Table of Content |
Key words: Tropism, Stimulus, Tropic, Plant, Movement, Phototropism, Gravitropism, Chemotropism, Thigmotropism, Hydrotropism, Thermotropism
Read More: Inclusion Bodies
Tropic Movements
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
When a plant unveils some growth movement in response to a stimulus, it is known as tropism. Tropism is specific to the direction of the stimulus, and in response to a stimulus, plants can either display a negative or positive movement. When the movement is towards the direction of stimuli, It is positive tropism while it is negative tropism when the movement is away from the stimuli.
Also read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Binary Fission | Asexual Reproduction | Double Fertilzation |
Types of Tropism
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are 6 basic types of tropic movements observed in plants as identified by their response to an external stimulus:
- Phototropism
- Gravitropism
- Chemotropism
- Thigmotropism
- Thermotropism
- Hydrotropism
Tropic movements are crucial for plant survival and all the metabolic activities are dependant on environmental factors.
Also Read:
Phototropism
All living organisms must prepare their food. Plants too prepare their food by the well-known process of photosynthesis. Hence, sunlight is a crucial element for this process to happen. The sunlight here, is a natural stimulant, in response to which the plant parts such as leaves, stem, and shoot grow towards the direction of sunlight(positive tropism), and the root moves away from it (negative tropism).
- This directional movement of plant parts in response to a light source is called Phototropism.
- A very classic example is the sunflower.
But how this movement is caused?
Auxin is a plant hormone responsible for its growth.
- This hormone allows the leaves to bend forward towards the light source to efficiently carry out photosynthesis.
- Plants can be seen to form a curvature around the stem region while the growth happens in the direction of light.
- Similarly, the roots tend to move away from the light source into the soil.
Also read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Flower Structure | Fragmentation in Plants | Gemmule Formation |
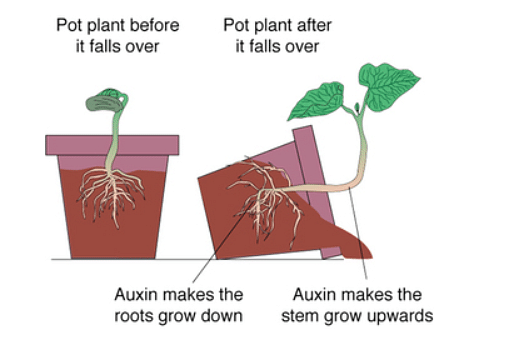
Gravitropism
Plant growth vertically downwards or against gravity is called Gravitropism or Geotropism. Parts such as the primary roots and their subparts tend to direct their growth towards the center of gravity (positive geotropism).
- However, the stem and shoot move away from the soil and grow upwards (negative geotropism).
- Leaves on the other hand grow transversely which is in right angles to the center of gravity.
- Hence they are said to be transversely geotropic.
- Some interesting examples are prostrate shrubs wherein the stem loses negative geotropism as it grows and develops into tubes or root stocks thereby displaying positive geotropism.
Read More:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Components of Ecosystem | Food Chains and Webs | Ozone Layer |
Chemotropism
Tropic movement in plants caused by certain chemical substances is called Chemotropism. This is a common growth phenomenon observed in flowering plants.
- Certain chemicals secreted by the plants bring about changes in the growth direction.
- These movements could be seen as curvatures in plant stems or downward growth style of the pollen tubes.
- Sessile plants use chemotropism for reproduction.
- The insect or wind transferred pollen grains that are planted in the pollen tubes cause tube elongation in the downward direction.
- This is due to a chemical secretion from the plant ovaries.
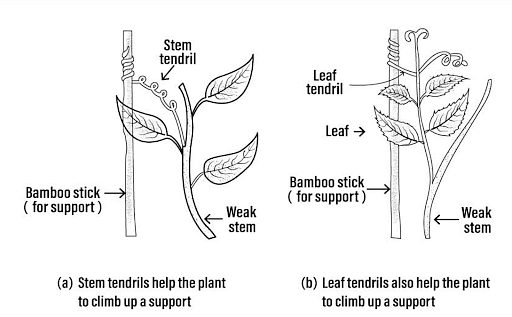
Thigmotropism
When a plant comes into contact with a solid object, it tends to take its help and grow in the same direction. This growth response is called thigmotropism. Usually, plants with tendrils or twiners have weak stems that do not allow the plant to stay upright. An external solid object or a surface facilitates such plants to stay firm and grow in the direction of the support.
Read More:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Microsporangia | Megasporangia | Haplontic Life Cycle |
An example of this kind of tropic movement is seen in Venus Flytrap whose leaves shut as soon as the prey gets trapped inside.

Thermotropism
When atmospheric variation in temperature acts as a stimulus and causes the plant to move towards a specific direction (positive or negative) is called Thermotropism. This movement effectively explains the growth of roots in plants. The soil that is closer to the ground surface is warmer than the deeper layers. Hence, in plants like Zeemays, the roots bend differently in soil layers. Similarly, the leaves of the Rhododendron bend when exposed to cold temperatures.

Hydrotropism
The variation in water concentration in the soil can also cause directional (positive or negative) movements in plants. This growth or movement tendency towards a water stimulus is called Hydrotropism.
- Every plant needs water for carrying out its metabolic activity.
- The roots in plants, hence absorb water in the soil and tend to grow in the direction of the water source.
- This kind of tropism helps the plant to overcome extreme drought conditions and against over-saturation.
-
Researches have shown the existence of diverse stimuli in our environment like growth in the direction of certain colors of light, with respect to humidity or seasonal changes, etc.
Growth or movement responses to these have been mapped to specific tropism types. This involuntary orientation of plants facilitates their adjustment with environmental conditions and allows food preparation, adequate mineral and water absorption that is necessary for their survival.

Also read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parthenocarpy | Pollination | Cyanobacteria |
| Polyembryony | Sporulation | Saprophytes |
Things to Remember
- Directional response to environmental stimulus in organisms causes their growth or movement. This is called
- Tropism can be positive (towards stimulus) or negative (away from the stimulus).
- In plants, 6 basic types of tropism are observed: Phototropism- a directional movement/ growth towards or away from the light source
- Gravitropism- A directional movement/ growth towards or away from the center of gravity
- Chemotropism- A directional movement/growth in reaction to certain chemical substances
- Thigmotropism- A directional movement/growth in response to contact with a solid surface or an object.
- Thermotropism- A directional movement/growth in response to changes in atmospheric temperature
- Hydrotropism- A directional movement/growth in response to water stimulus
Sample Questions
Ques: Explain tropism with a suitable example? (3 marks)
Ans: Directional movement of living organisms in response to a stimulus is termed tropism. In rooted organisms like plants, tropism occurs as a structural alteration at the organ level which is seen as growth. A few examples are, the growth of a plant’s shoot and stem towards the sunlight, inward folding of the Mimosa pudica (touch me not) plant upon a gentle touch, curling up of a vine tendril on the surface in contact.
Ques: Why is the significance of tropism in plants? (2 marks)
Ans: Growth in plants is dependant on a multitude of factors such as the food they make, absorption of minerals and water for their metabolical activities, availability of support for a secured movement, environmental factors such as sunlight, touch, gravity, etc. All these contribute to the survival of a plant in its natural habitat. Hence a directional growth movement, or, tropism is essential for the development and continuation of the species.
Ques: What causes tropism to be positive or negative? (2 marks)
Ans: The growth and movement of a plant in response to an environmental stimulus are controlled by the direction of the stimulus striking the plant. Hence, when the growth tends to be towards the stimulus, it is known as positive tropism and when growth is away from the stimulus, it is called negative tropism. For example, the stem of a plant shows positive tropism (towards sunlight) and the root shows negative tropism (away from light).
Ques: Illustrate using simple diagrams: phototropism, geotropism, and hydrotropism? (5 marks)
Ans: Phototropism

(a) and (b) show how the plant movement or growth occurs in response to a change in direction of sunlight
Geotropism

Roots bend towards the center of gravity and stem move away from the center of gravity
Hydrotropism

The pea plant roots grow towards the higher water concentration region and absorb water for carrying out the plant metabolic activities
Ques: How does the root of a plant play an important role in carrying out the metabolic activities through tropism? (2 marks)
Ans: Plants take in essential growth nutrients and water from the soil with the help of their roots. Based on the concentration of water in the soil, the plant roots tend to bend towards or away from the source based on the requirement. This growth movement helps the plant to protect itself from extreme drought conditions (moves towards the water stimulus) or from dying caused by oversaturation due to excess water absorption.
Ques: Mention the role of the plant hormone Auxin? (3 marks)
Ans: Plants are immobile organisms. To perform basic functions such as the preparation of food by photosynthesis, plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Auxin is a plant hormone found in the shoot and root tips that facilitate cell elongation in the stem of a plant. This allows directional growth causing the stem tip to form a curvature towards the sunlight direction. Hence, the leaves are exposed to more light for efficient photosynthesis.
Ques: Explain Thigmotropism with a simple illustration and appropriate labeling? (3 marks)
Ans: The directional growth movements occurring in plants in response to touch are called Thigmotropism. A simple example of this is the Touch Me Not or the Mimosa Pudica plant whose leaves bend inwards in response to touch. Plants with tendrils or twiners also display Thigmotropism. The stems of these plants are very weak and to stay upright and grow, they take support of the surface or object they come in contact with.
Read More: Translation in Biology
Do Check Out






Comments