
Content Writer
Saturated Solution refers to a chemical solution that contains the maximum concentration of a solute dissolved in the solvent. No additional amount of solute will be able to dissolve in a saturated solution. Further addition of solute after reaching the saturation point would result in a solid precipitate or gas being released. It depends on a variety of factors on how much amount of solute can be dissolved in a solvent to form a saturated solution.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Saturated Solutions, Solutions, Unsaturated Solutions, Supersaturated Solutions, Saturation Point, Solubility
What are Saturated Solutions?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Saturated Solution is one of the three types of solutions named unsaturated solutions, saturated solutions and supersaturated solutions.
A saturated solution is defined as a solution which contains the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved under the same condition in which the solute is dissolved. This happens when a solution reaches the point where we cannot add more amount of solute to it. In case more amount of solute is added after this point, a solid precipitate or gas will be released.
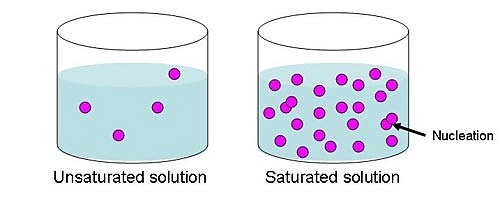
Saturated and Unsaturated Solution
Read More:
| Chapter-Related Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Concentration of a Solution | Types of Solutions | Colloidal Solutions |
| Pressure of an Ideal Gas | Mixtures | Ideal Solution |
How to Prepare Saturated Solutions?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
In order to make a saturated solution, we have to add the solute into the solution until it reaches a point where the whole solution reacts as a solid precipitate and crystals to form a highly saturated solution. The steps to make a saturated solution are as follows:
- Step 1: Let’s consider an example that we use in daily life which is adding sugar to a container of water.
- Step 2: Primarily, as the solution is stirred, the added sugar dissolves.
- Step 3: Eventually, a point is reached where no amount of stirring will cause the added sugar to dissolve as more sugar has been added.
- Step 4: The last added sugar continues to exist as a solid at the bottom of the container, and the solution is saturated.

Preparation of Saturated Solution
Factors Affecting Saturation Solution
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The amount of solute dissolving to form a saturated solution in a solvent depends on a variety of factors among which the most important factors are as follows:
- Temperature: Solubility increases as the temperature increases. When the temperature is increased, then solutions for the ionic atoms are also increased.
- Pressure: Increasing pressure can force more solute into the solution. This is commonly used to dissolve gases into liquids.
- Chemical composition: Solubility is affected by the nature of the solute and solvent and the presence of other chemicals in a solution. For instance, we can dissolve much more sugar in water than salt in water. Ethanol and water are completely soluble in each other.
- Le Chatelier’s principle is used to predict the response of the equilibrium system which is based on the change in pressure, concentration and temperature.

Examples of Saturated Solutions
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Here are a few real-life examples of saturated solutions:
- In beverages there is water that is treated as a solvent and carbon air is treated as a solute in the solution until saturation is reached.
- In kitchen-oriented things also, like cooking recipes involve dissolving salt, sugar or other household ingredients into the water. The whole process is temperature-dependent. As the temperature of water increases the solubility of the solute also increases. After the point saturation is reached, the solute acts as a visible layer on top of the solvent.
- Soil found on the earth’s surface is also considered to be a saturated mixture that consists of nitrogen. Once the saturation point is reached, the excess nitrogen is emitted into the air in the form of gas.
Types of Saturation
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A solution can be classified into three main types based on its saturation. The three types are as follows:
- Saturated Solution: The type of solution where an equilibrium is there with respect to the dissolved substance is called a saturated solution. It means no more solute can be added to the solution. Carbonated water is the best example of this type of solution.
- Unsaturated Solution: The type of solution where equilibrium is not there with respect to the dissolved substance is called a saturated solution. It means more solute can be dissolved into the solution. Sodium chloride in water is the best example of this type of saturation.
- Supersaturated Solution: This type of solution contains more dissolved substances than saturated solutions. While making tea we add sugar into the water is the best example of a supersaturated solution.

Types of Saturation
Things to Remember
- A saturated solution is referred to as one of the three types of solutions named saturated solutions, unsaturated solutions, and supersaturated solutions.
- A saturated solution is defined as a solution where the maximum amount of solute has been added and no more solute can be added to the same.
- If more amount of solute is added after reaching the saturation point, it would result in the release of solid precipitate or gas
- An unsaturated solution is a solution where there is no equilibrium with respect to the dissolved substance.
- In supersaturated solution, it contains more dissolved substance than saturated solutions.
- The amount of solute dissolving to form a saturated solution in a solvent depends on a variety of factors among which the most important factors like temperature, pressure, and chemical composition.
Read More:
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
- When 25 g of a non-volatile solute is dissolved in 100 g of water… (BITSAT 2008)
- 0 .15 g of a substance dissolved in 15 g of a solvent higher by… (NEET 1999)
- 200 mL of an aqueous solution of a protein contains its… (NEET 2011)
- At 25∘C, the highest osmotic pressure is exhibited by… (NEET 1994)
- A 5% solution of cane sugar (MW = 342) is isotonic with… (NEET 1998)
- At 100∘C, the vapour pressure of a solution of 6.5g of a solute in… (NEET 2016)
- A solution of acetone in ethanol… (NEET 2006)
- For determination of molar mass of colloids,polymers and protein… (NEET 2000)
- An ideal solution is formed when its components… (NEET 1998)
- In water saturated air the mole fraction of water vapour is… (NEET 2019)
Sample Questions
Ques. List down the three types of solutions. (3 Marks)
Ans. On the basis of the saturation level, a solution can be classified into three types:
- Saturated Solutions
- Unsaturated Solutions
- Supersaturated Solutions
Ques. What are the factors that affect the saturation level of a solution? (3 Marks)
Ans. The saturation level of a solution is affected by the following factors:
- Temperature: When the temperature is increased, the solubility increases.
- Pressure: More solute can be forced into a solution by increasing pressure.
- Chemical Composition: The nature of the solute and solvent affects the solubility along with the involvement of other contaminants in a solution.
Ques. A mixture that has a uniform composition throughout is called
(A) Saturated Solution
(B) Supersaturated Solution
(C) Solution
(D) Solvent (1 Mark)
Ans. (C) Solution
Ques. At a particular temperature, the solution which cannot dissolve more solute is called
(A) Saturated Solution
(B) Unsaturated Solution
(C) Aqueous Solution
(D) Supersaturated Solution (1 Mark)
Ans. (A) Saturated Solution
Ques. Define supersaturated solutions. (2 Marks)
Ans. Supersaturated solutions contain more dissolved solute than allowed for making a saturated solution. A supersaturated solution is formed by heating a saturated solution and then adding more solute, and lastly allowing it to cool down.
Ques. State the difference between saturated and unsaturated solutions. (3 Marks)
Ans. A saturated solution is a solution where the maximum amount of solute has been dissolved and if we add any additional amount of solute to it, then, it would not dissolve and lead to the formation of solid precipitate or a gas.
An unsaturated solution is a solution where the solute concentration is lesser than its equilibrium solubility. It means that the amount of solute is in lesser amounts than its saturation level.
Ques. How is a supersaturated solution formed? (2 Marks)
Ans. A solution can be turned into a supersaturated solution by dissolving the solute in water at a higher temperature using enough to give a concentration just under its solubility at that temperature. At last, the solution is allowed to cool after the last of the solute crystals have dissolved.
Ques. Give an example of saturated and unsaturated solutions each. (3 Marks)
Ans. Soda drink is an excellent example of a saturated solution. It is a saturated solution of carbon dioxide in water. That’s the reason when we open a can or bottle of soda, the pressure is released, and carbon dioxide gas forms bubbles.
An example of an unsaturated solution would be adding a spoonful of sugar to a cup of hot coffee. Another example would be vinegar which is an unsaturated solution of acetic acid in water.
Ques. How can we prepare a saturated solution? (5 Marks)
Ans. In order to make a saturated solution, follow the given steps:
- Take salt for instance and add a spoon of salt to a glass of water.
- Keep on adding the salt and you will notice that it keeps on dissolving.
- Now, there will be a point where the salt will not be able to dissolve no matter how much you stir the solution.
- Finally, the last added salt crystals will remain as a solid on the bottom of the container, which means that the solution is saturated.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments