The compressibility factor for a real gas at high pressure is :
- $1 + RT/Pb$
- $1$
- $1 + Pb /RT$
- $1 - Pb/RT$
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on Van Der Waals equation
- Which of the following statemnt is incorect for physisorption?
- GUJCET - 2023
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- Arrange the following gases in increasing order of van der Waals constant 'a'
A. Ar
B. CH4
C. H₂O
D. C6H6
Choose the correct option from the following.- JEE Main - 2023
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- At low pressure, the van der Waal's equation is reduced to
- VITEEE - 2019
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- Given van der Waals constant for NH3, H2, O2 and CO2 are respectively 4.17, 0.244, 1.36 and 3.59, which one of the following gases is most easily liquefied ?
- NEET (UG) - 2018
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
- If $V$ is the volume of one molecule of gas under given conditions, the van der Waal?s constant $b$ is
- BITSAT - 2018
- Chemistry
- Van Der Waals equation
Questions Asked in AIEEE exam
- A steel wire can sustain $100\, kg$ weight without breaking. If the wire is cut into two equal parts, each part can sustain a weight of
- AIEEE - 2012
- mechanical properties of solids
- The limiting line in Balmer series will have a frequency of (Rydberg constant, $R_{\infty}=3.29\times10^{15}$ cycles/s)
- AIEEE - 2012
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Which of the plots shown in the figure represents speed (v) of the electron in a hydrogen atom as a function of the principal quantum number (n)?
- The ratio of number of oxygen atoms (O) in 16.0 g ozone $(O_3), \,28.0\, g$ carbon monoxide $(CO)$ and $16.0$ oxygen $(O_2)$ is (Atomic mass: $C = 12,0 = 16$ and Avogadro?? constant $N_A = 6.0 x 10^{23}\, mol^{-1}$)
- AIEEE - 2012
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
Liquids A and B form an ideal solution at 30°C, the total vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mol of A and 2 mol of B is 250 mmHg. The total vapour pressure becomes 300 mmHg when 1 more mol of A is added to the first solution. The vapour pressures of pure A and B at the same temperature are
- AIEEE - 2012
- Solutions
Concepts Used:
Van Der Waals Equation
Van der Waals equation is an equation relating the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of real gases.
Read More: Derivation of Van Der Waals Equation
Derivation of Van der Waals equation:
For a real gas containing ‘n’ moles, the equation is written as
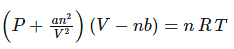
Where, P, V, T, n are the pressure, volume, temperature and moles of the gas. ‘a’ and ‘b’ constants specific to each gas.
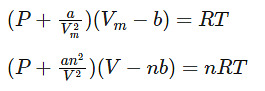
Where,
Vm: molar volume of the gas
R: universal gas constant
T: temperature
P: pressure
V: volume
Thus, Van der Waals equation can be reduced to ideal gas law as PVm = RT.
The equation can further be written as;
- Cube power of volume:
- Reduced equation (Law of corresponding states) in terms of critical constants:
Units of Van der Waals equation Constants
a: atm lit² mol-²
b: litre mol-¹



