Pure line breed refers to
Show Hint
Pure line breeding is a breeding method that involves a group of individuals with identical traits consistently producing offspring with the same characteristics.
- heterozygosity only
- heterozygosity and linkage
- homozygosity only
- homozygosity and self assortment
The Correct Option is C
Approach Solution - 1
Pure line breeding involves a group of identical individuals that consistently produce offspring with the same characteristics when intercrossed. This breeding method relies on homozygous individuals, meaning they have two identical alleles for a particular gene.
- Both mating breeds in pure line breeding are pure lines themselves, consisting of generations of homozygous individuals.
- The offspring produced through pure line breeding exhibit the same genotype and phenotype as their parents, ensuring the breeding line remains consistent.
- Pure line-breeding results in true breeding genotypes, where homozygous individuals only produce offspring that are also homozygous for the same traits.
- The term "pure line breed" essentially refers to the condition of homozygosity, ensuring the offspring consistently display the desired traits.
Therefore, Option C is the correct answer.
Discover More From the Chapter: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Approach Solution -2
Pure line breeding is a breeding method that involves a group of individuals with identical traits consistently producing offspring with the same characteristics. This breeding method ensures the maintenance of desirable traits in subsequent generations.
Homozygosity in Pure Line Breed
- Homozygosity is a key feature of pure-line breeding.
- Homozygous individuals possess two identical alleles for a particular gene.
- This means they are genetically uniform for that trait.
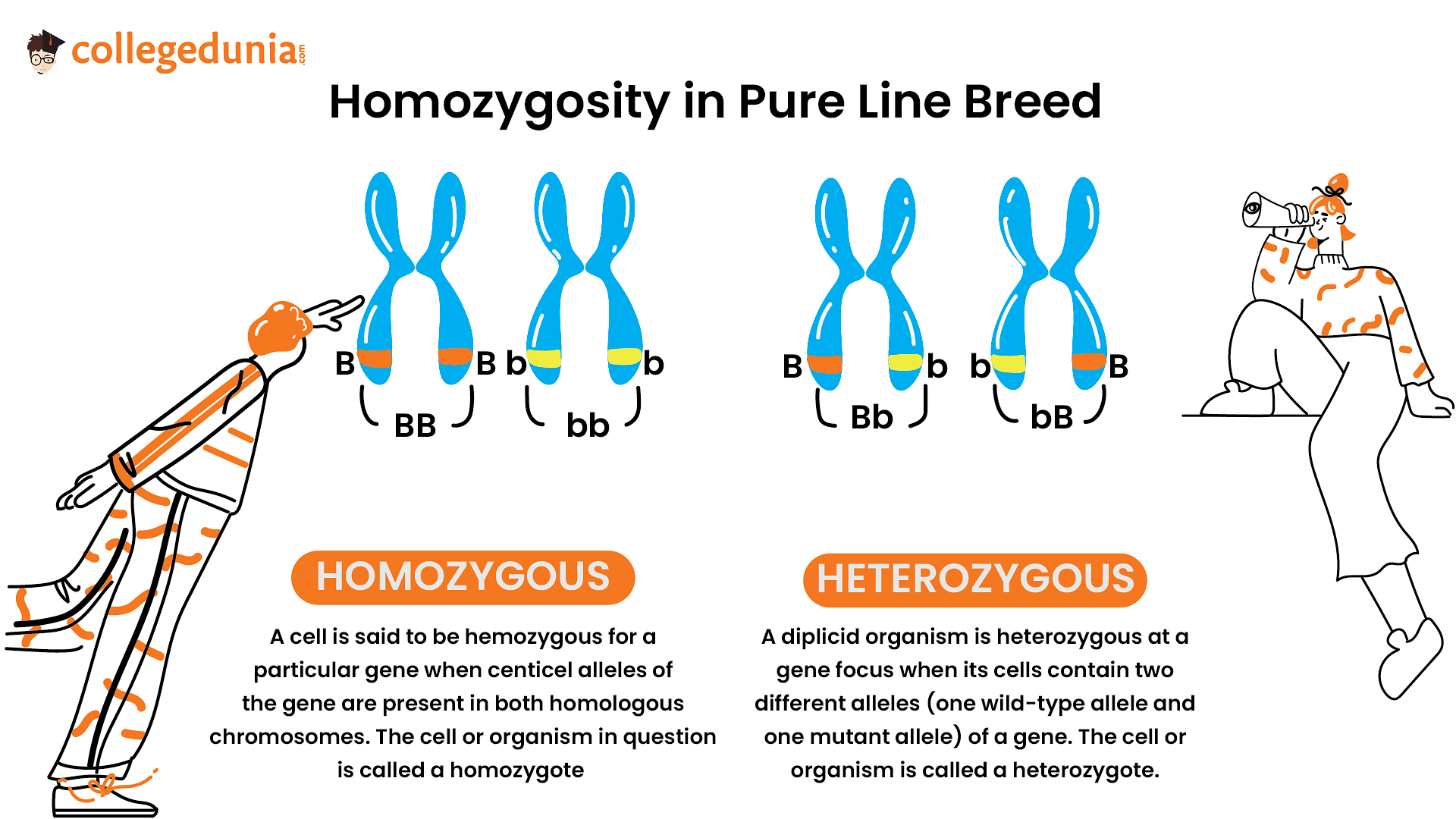
Consistency in Genotype and Phenotype
- Pure line breed relies on generations of homozygous individuals.
- When intercrossed, these homozygous individuals produce offspring with the same genotype and phenotype as their parents.
Read More:
| Related Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | Bones of Legs | Pollination by Snails |
| Peroxisomes | Neuroscience | Paralysis Symptoms |
| Phospholipid | Nutrition in Amoeba | Micro Propagation |
True Breeding Genotypes
- Pure line-breeding results in true breeding genotypes, where homozygous individuals consistently produce offspring that are also homozygous for the same traits.
- This ensures the breeding line remains consistent and stable in terms of genetic characteristics.
Pure line breeding allows for the focused breeding of individuals with specific traits. By selecting and mating homozygous individuals with desired traits, breeders can maintain and perpetuate those traits in subsequent generations.
Top Questions on Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- If there were 100 rose plants in a garden last year. 20 new rose plants are added through reproduction in current year. the birth rate of rose is ____ offspring per rose per year.
- CUET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- If a pink flowered snapdhagon plant is crossed with a white flowered snapdragan plant. What will be the phenotype of their progen ?
- CUET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Which of the following statements are correct about Klinefelter’s Syndrome?
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866).
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine development is also expressed.
C. The affected individual is short statured.
D. Physical, psychomotor and metal development is retarded. E. Such individuals are sterile.Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Which one of the following symbols represents mating between relatives in human pedigree analysis?
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- The phenomenon of pleiotropism refers to
- NEET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Questions Asked in AIIMS exam
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion (A) : 02 is liberated in the non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Reason (R) : Liberation of oxygen is due to photolysis of water.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
- AIIMS - 2019
- Photosynthesis in higher plants
- Match the following column I with column II.
- AIIMS - 2019
- cloning
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion (A) : The Cro-Magnon man was the direct ancestor of the living modern man.
Reason (R) : Cro-Magnon man had slightly prognathous face.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
- AIIMS - 2019
- evolution
- Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion: Orbit of a satellite is within the gravitational field of earth whereas escaping is beyond the gravitational field of earth.
Reason: Orbital velocity of a satellite is greater than its escape velocity.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below- AIIMS - 2019
- Gravitation
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion (A) : In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in nucleus.
Reason (R) : In bacteria, transcription and translation occurs in cytoplasm.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
- AIIMS - 2019
- Transcription
Concepts Used:
Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Mutation
A Mutation is a change in the sequence of our DNA base pairs caused by numerous environmental stimuli such as UV light or mistakes during DNA replication. Germline mutations take place in the eggs and sperm and can be passed onto offspring, whereas somatic mutations take place in body cells and are not passed on.
Types of Mutations
There are three types of mutations, which are as follows:
Silent mutation
It refers to any change in DNA sequence that has no effect on the amino acid sequence in a protein or the functions that a protein performs. There is no phenotypic indication that a mutation has occurred.
Nonsense mutation
When there is a change in the sequence of base pairs due to a point mutation, that results in a stop codon. This leads to a protein that is either shortened or non-functional.
Missense mutation
A missense mutation occurs when a point mutation causes a change in the codon, which then codes for another amino acid.
The mutation is caused by the following factors:
Internal Causes
When DNA copies incorrectly, the majority of mutations occur. Evolution occurs as a result of all of these mutations. DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division. When a copy of DNA isn't flawless, it's called a mutation since it differs somewhat from the original DNA.
External Causes
When certain chemicals or radiations are used to break down DNA, it causes the DNA to break down. The thymine dimers are broken by UV radiation, resulting in altered DNA.



