A uniform electric field of $10 N / C$ is created between two parallel charged plates (as shown in figure) An electron enters the field symmetrically between the plates with a kinetic energy $05 eV$ The length of each plate is $10 cm$ The angle $(\theta)$ of deviation of the path of electron as it comes out of the field is ___ (in degree)


Correct Answer: 45
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is 45
0.5e \(=\frac{1}{2}\ mv^{2}_x\) ⇒ vx \(=\sqrt{\frac{e}{m}}\)
Along x L = vxt \(=\sqrt{\frac{e}{m}t}\)
Along y vy = \(\frac{eE}{m}t\)
dividing \(\frac{v_y}{L}=E\sqrt{\frac{e}{m}}=Ev_x\)
⇒ Tan \(\theta=\frac{v_y}{v_x}=E\times L=10\times0.1=1\)
\(\theta=45°\)
Top Questions on Electric charges and fields
- Two particles each of mass \(2\) kg are places as shown in \(x→ y\) plane. If the distance of centre of mass from origin is \(\frac{4\sqrt 2}{x}\) find \(x\) :
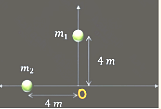
- JEE Main - 2024
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
- Electric field in a certain region is given by $\overrightarrow{ E }=\left(\frac{ A }{x^2} \hat{i}+\frac{ B }{y^3} \hat{j}\right)$ The $SI$ unit of $A$ and $B$ are :
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
Given below are two statements : One is labelled as Assertion $A$ and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A : Two metallic spheres are charged to the same potential One of them is hollow and another is solid, and both have the same radii Solid sphere will have lower charge than the hollow one
Reason R : Capacitance of metallic spheres depend on the radii of spheres
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given belows- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
- A condenser of $2 \,\mu F$ capacitance is charged steadily from $0$ to $5 C$ Which of the following graph represents correctly the variation of potential difference $(V)$ across it's plates with respect to the charge $( Q )$ on the condenser?
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
- A 10 μC charge is divided into two equal parts and kept at 1 cm distance. Find repulsion between charges?
- JEE Main - 2023
- Physics
- Electric charges and fields
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
- Let \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k}, \quad \vec{b} = -\hat{i} - 8\hat{j} + 2\hat{k}, \quad \text{and} \quad \vec{c} = 4\hat{i} + c_2\hat{j} + c_3\hat{k} \]be three vectors such that \[\vec{b} \times \vec{a} = \vec{c} \times \vec{a}.\]If the angle between the vector $\vec{c}$ and the vector $3\hat{i} + 4\hat{j} + \hat{k}$ is $\theta$, then the greatest integer less than or equal to $\tan^2 \theta$ is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Vector Algebra
- 10 mL of gaseous hydrocarbon on combustion gives 40 mL of CO\(_2\)(g) and 50 mL of water vapour. The total number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon is ______ .
- JEE Main - 2024
- Hydrocarbons
- If each term of a geometric progression \( a_1, a_2, a_3, \dots \) with \( a_1 = \frac{1}{8} \) and \( a_2 \neq a_1 \), is the arithmetic mean of the next two terms and \( S_n = a_1 + a_2 + \dots + a_n \), then \( S_{20} - S_{18} \) is equal to
- JEE Main - 2024
- Arithmetic Mean
A body of mass 1000 kg is moving horizontally with a velocity of 6 m/s. If 200 kg extra mass is added, the final velocity (in m/s) is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- speed and velocity
- $\textbf{Choose the correct statements about the hydrides of group 15 elements.}$
A. The stability of the hydrides decreases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 > \text{PH}_3 > \text{AsH}_3 > \text{SbH}_3 > \text{BiH}_3\)
B. The reducing ability of the hydrides increases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 < \text{PH}_3 < \text{AsH}_3 < \text{SbH}_3 < \text{BiH}_3\)
C. Among the hydrides, \(\text{NH}_3\) is a strong reducing agent while \(\text{BiH}_3\) is a mild reducing agent.
D. The basicity of the hydrides increases in the order \(\text{NH}_3 < \text{PH}_3 < \text{AsH}_3 < \text{SbH}_3 < \text{BiH}_3\)
Choose the most appropriate from the option given below:- JEE Main - 2024
- p -Block Elements
Concepts Used:
Electric charges and field
What is Electric Charge
It is the property of subatomic particles that experiences a force when put in an electric and magnetic field.
What is Electric Field
It is a property associated with each point in space when charge is present in any form. The magnitude and direction of the electric field are expressed by E, called electric field strength or electric field intensity.
Electric charges are of two types: Positive and Negative. It is commonly carried by charge carriers protons and electrons.
Properties of Electric Charge
Various properties of charge include the following :-
- Additivity of Electric Charge
- Conservation of Electric Charge
- Quantization of Electric Charge
Types of electric charge
Two kinds of electric charges are there :-
Negative Charge - When an object has a negative charge it means that it has more electrons than protons.
Positive Charge - When an object has a positive charge it means that it has more protons than electrons.
When there is an identical number of positive and negative charges, the negative and positive charges would cancel out each other and the object would become neutral.



